Amazon ECS Explorer
Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a fully managed container orchestration service that helps you easily deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications. As a fully managed service, Amazon ECS comes with AWS configuration and operational best practices built in.
It's integrated with both AWS tools, such as Amazon Elastic Container Registry, and third-party tools, such as Docker. This integration makes it easier for teams to focus on building applications rather than managing the environment. You can run and scale your container workloads across AWS Regions in the cloud and on-premises, without the complexity of managing a control plane.
Prerequisite
- Set up ECS integration & AWS Integration (with
Amazon ECSnamespace enabled) to enable ECS features in Middleware.
The ECS section, located inside the Infrastructure section, provides visibility into Amazon Elastic Container Service workloads by organizing ECS resources into five logical areas:
- Tasks: Shows running instances created from ECS task definitions. This view is useful when you want to understand what is currently running and how tasks are behaving at runtime.
- Tasks Definitions: Shows the configuration used to create ECS tasks. It includes container definitions, resource limits, networking settings, environment variables, and IAM roles.
- Service: It focuses on ECS services that manage long-running workloads. Services ensure that a specified number of tasks remain running and replace tasks when failures occur.
- Containers: It provides container-level visibility for workloads running inside ECS tasks. It shows container status, resource usage, image details, and logs.
- Clusters: It shows ECS clusters that provide compute capacity for tasks and services. It helps you understand overall cluster health and how workloads are distributed.
Each section focuses on a specific ECS resource and helps you understand runtime behaviour, configuration, logs, and application performance in a single workflow.
Tasks
The Tasks section helps you monitor running ECS tasks and investigate task-level behaviour. From this view, you can quickly identify active tasks, review resource usage, and open a task to see configuration, containers, logs, and related resources.
Tasks list
The Tasks list shows all tasks detected in your ECS environment for the selected time range.
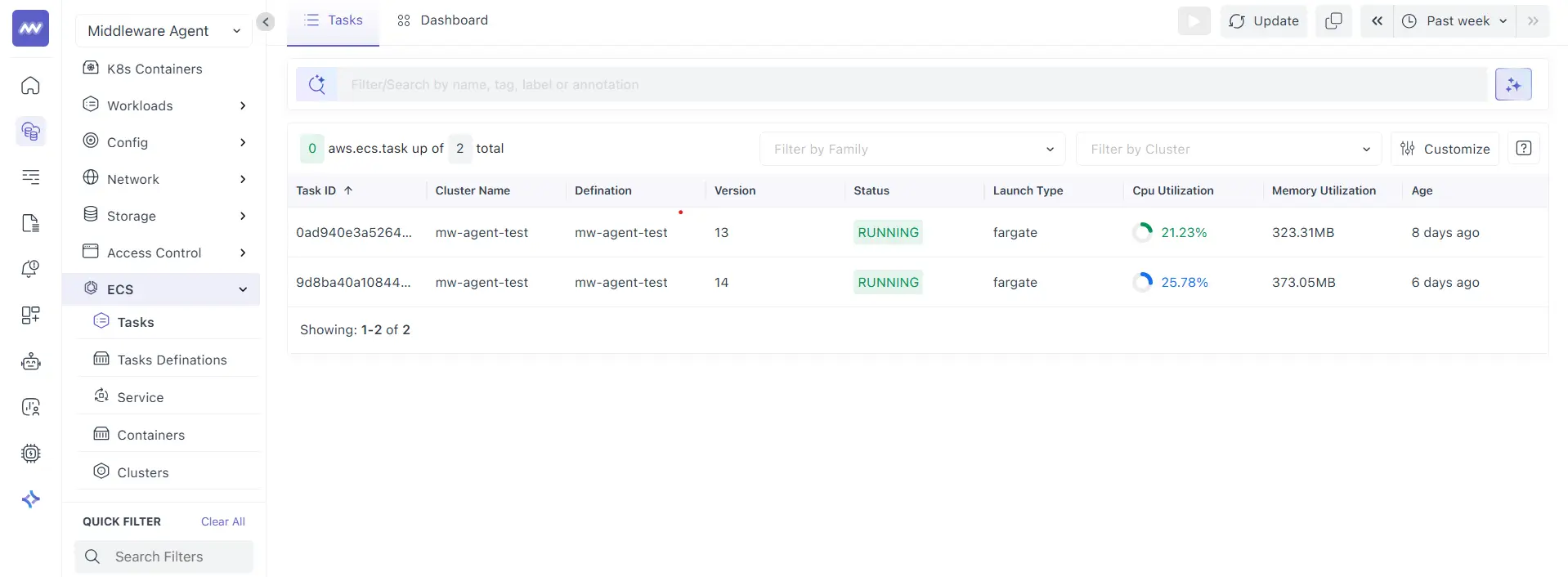
Each row represents a task. Common columns include:
- Task ID: The task identifier
- Cluster Name: The ECS cluster where the task is running
- Definition: The task definition family name
- Version: The task definition revision used by the task
- Status: Current task state, for example, RUNNING
- Launch Type: The launch type, for example, Fargate
- CPU Utilization: CPU usage is shown for the task
- Memory Utilization: Memory usage is shown for the task
- Age: How long ago the task started or was observed
Tasks Info
The Tasks Info tab provides a summary view of the selected task, along with key metrics and context.
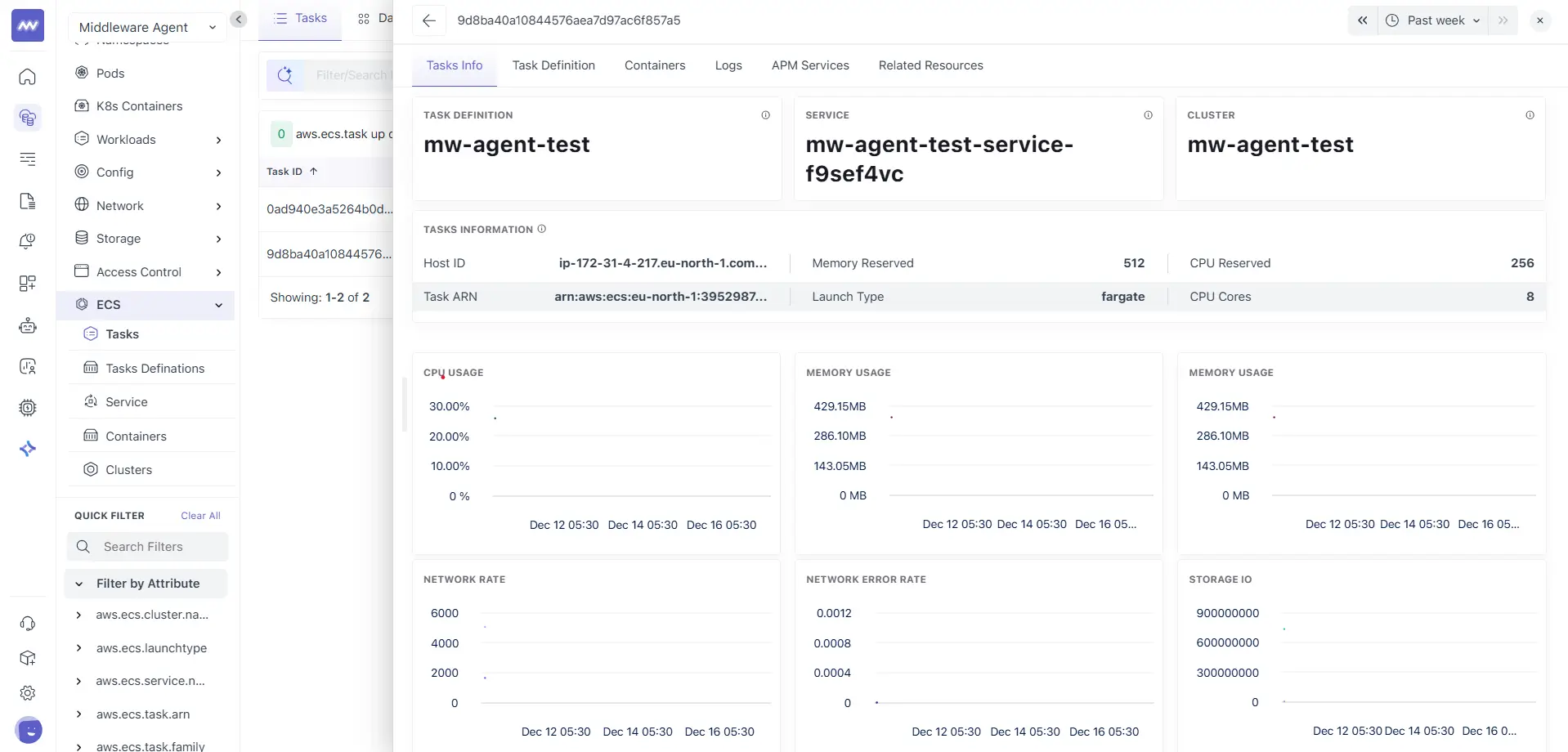
At the top, Middleware shows quick links to related ECS entities:
- Task Definition
- Service
- Cluster
These help you switch context without leaving the task view.
Task information
The task information section includes runtime metadata, such as:
- Host ID
- Task ARN
- Launch type
- CPU reserved
- Memory reserved
- CPU cores
Performance charts
This tab includes task-level charts that help you review behaviour over time, such as:
- CPU usage
- Memory usage
- Network rate
- Network error rate
- Storage IO
Use these charts to confirm whether the task is stable or experiencing spikes during the selected time range.
Task Definition
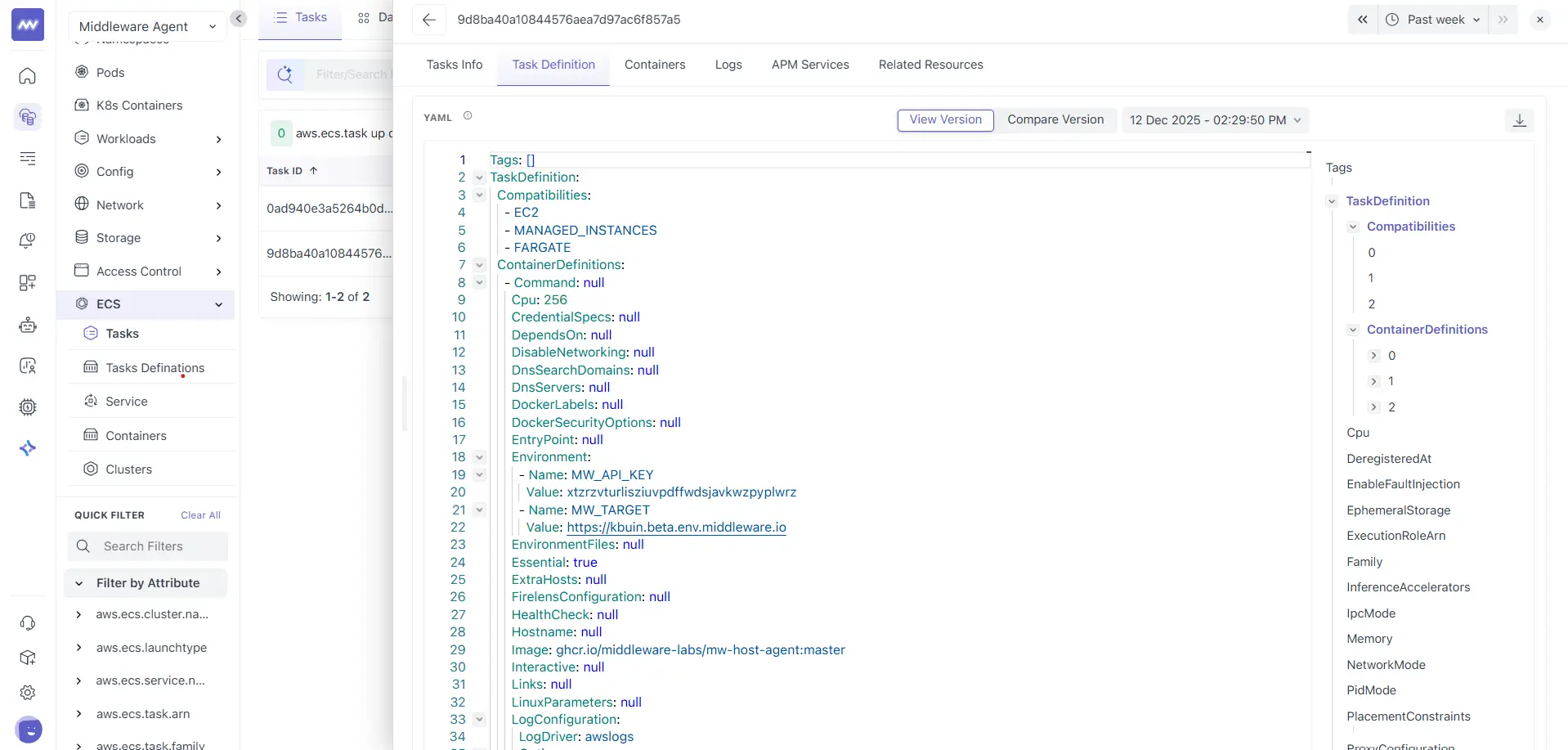
The Task Definition tab shows the configuration used to create the selected task and it shows:
- A YAML view of the task definition configuration, including container definitions and runtime settings
- A tags panel on the right that helps you browse and jump to specific sections
From here, you can:
- View Version lets you open a different version of the task definition
- Compare Version helps you review changes between versions
- The timestamp selector lets you view the configuration captured at a specific point in time
- The download option lets you export the configuration
This tab is useful when you need to connect runtime behaviour back to configuration, such as CPU and memory settings, image changes, or environment variables.
Containers
The Containers tab lists all containers running inside the selected task.
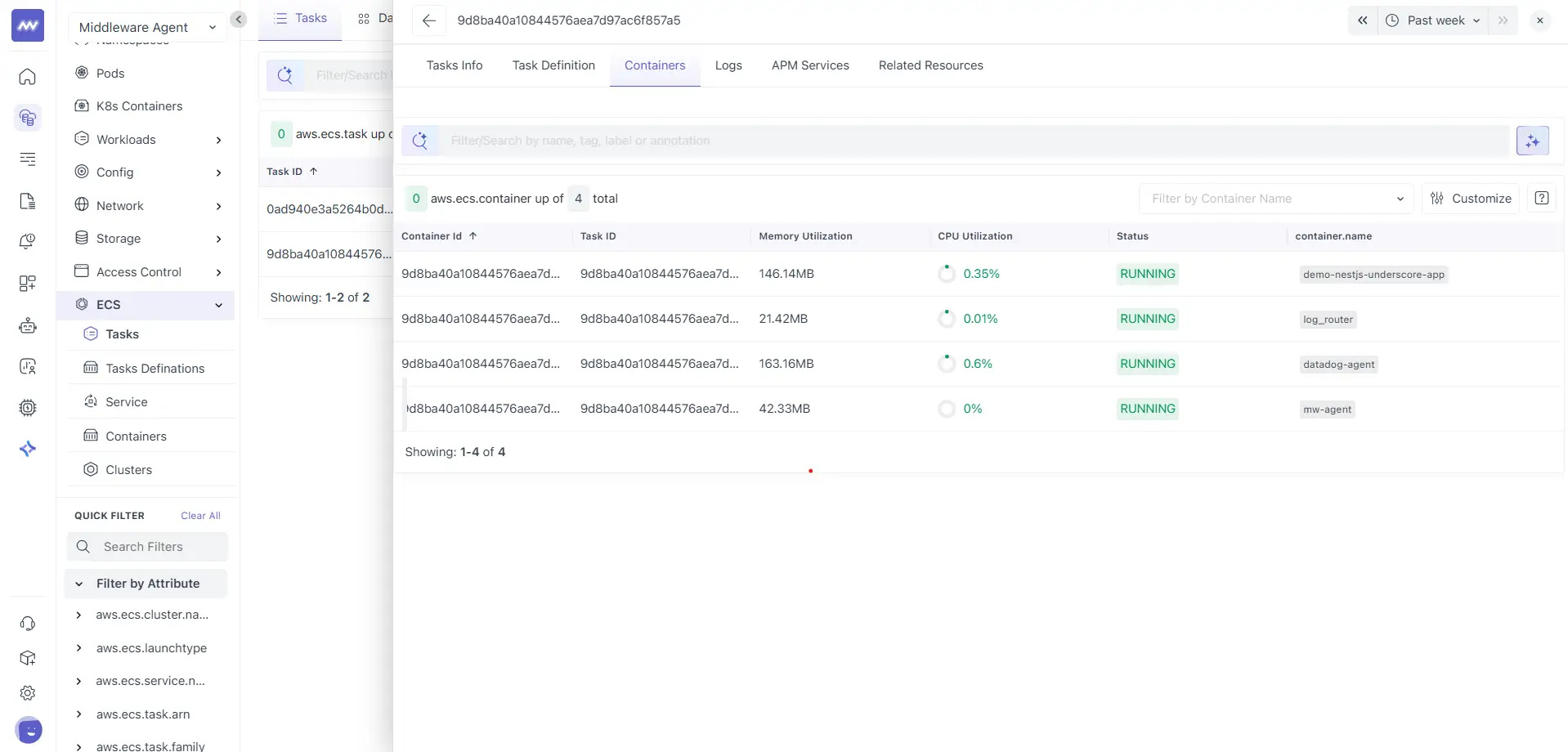
Here, each row represents a container running under the task. Common columns include:
- Container ID
- Task ID
- Memory utilization
- CPU utilization
- Status
- container.name
Click a container to open container-level details. This view contains two tabs: Container info and Logs.
Container Info
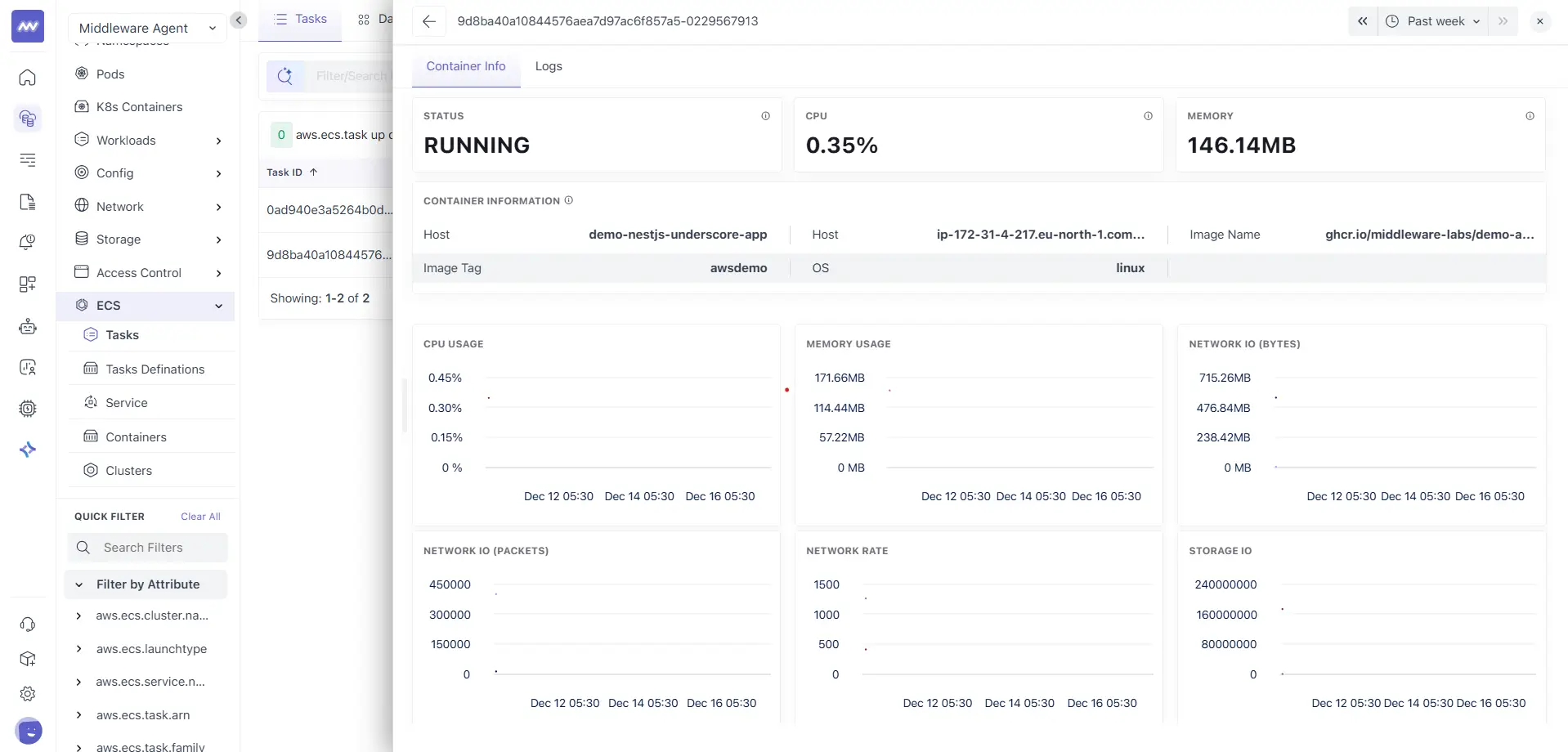
The Container Info tab provides a container-level summary and charts.
Summary tiles:
- Status
- CPU
- Memory
Container information: This section includes metadata such as:
- Host
- OS
- Image name
- Image tag
Performance charts: The charts help you validate container behaviour over time, including:
- CPU usage
- Memory usage
- Network IO in bytes
- Network IO in packets
- Network rate
- Storage IO
Use this view when a task is healthy, but one container is consuming more resources or behaving unexpectedly.
Container Logs
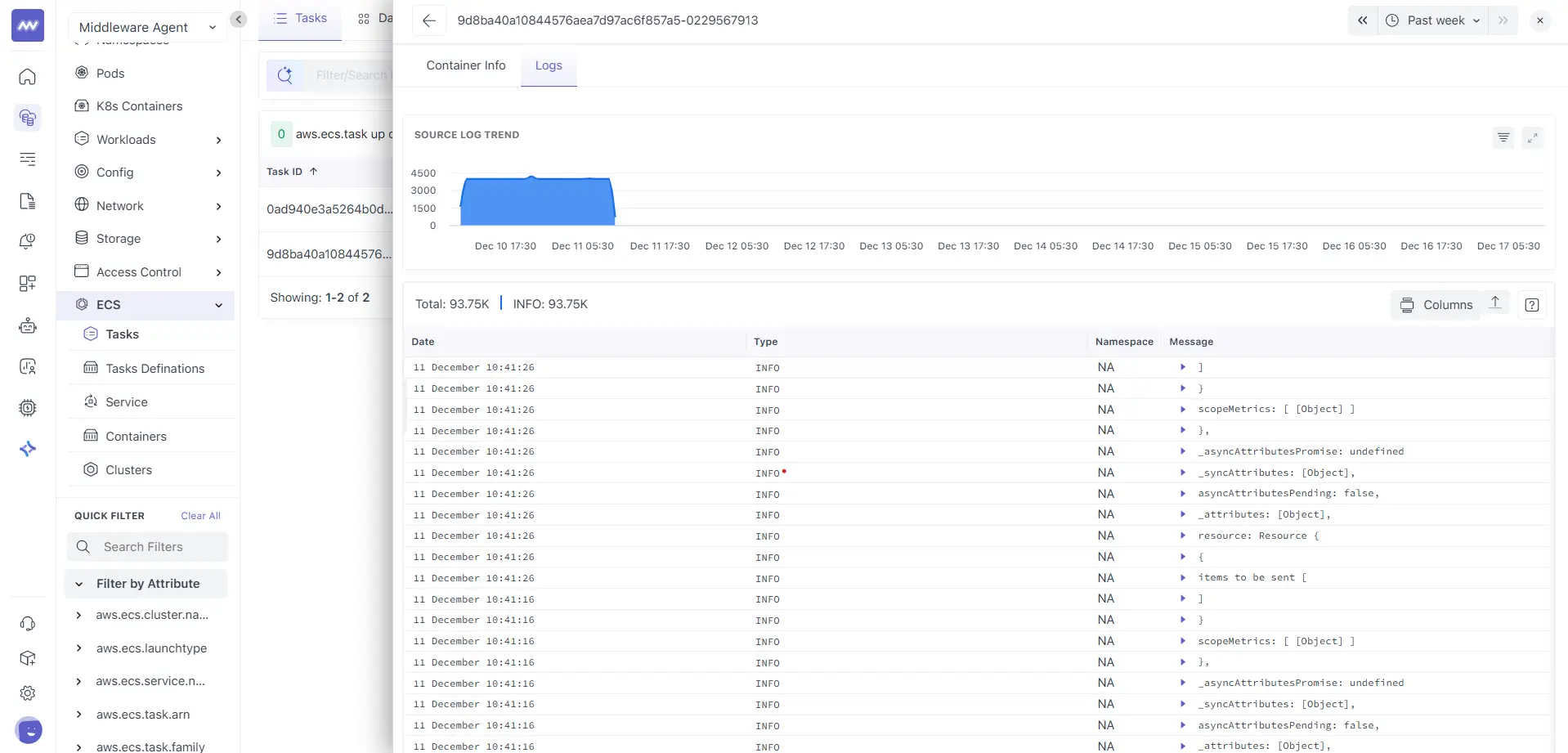
The Logs tab under a container shows logs for the selected container and shows you the following:
- A log trend chart for the selected time range
- A log table with common fields like timestamp, log type, and message
Use this view for fine-grained debugging when you already know which container is involved.
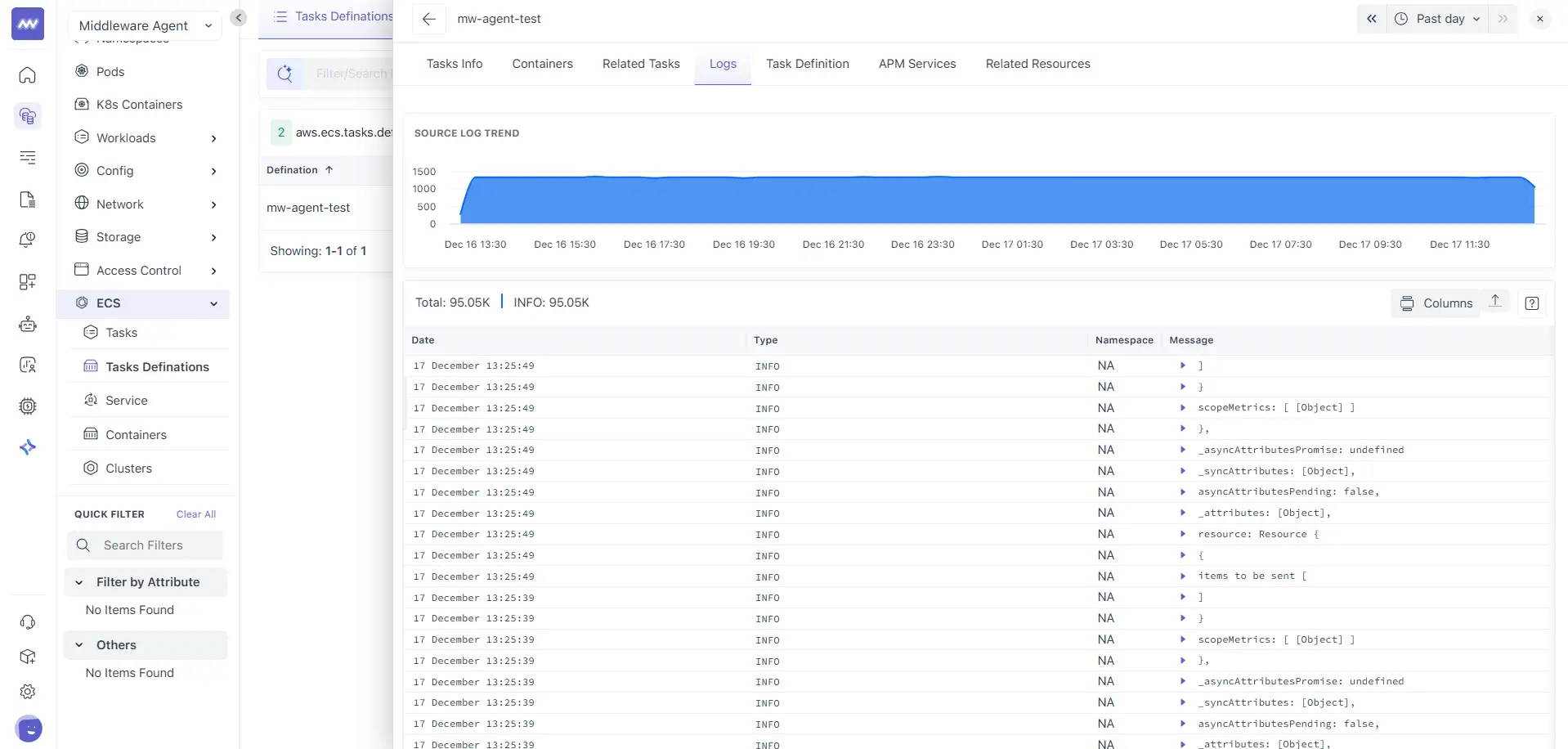
Logs
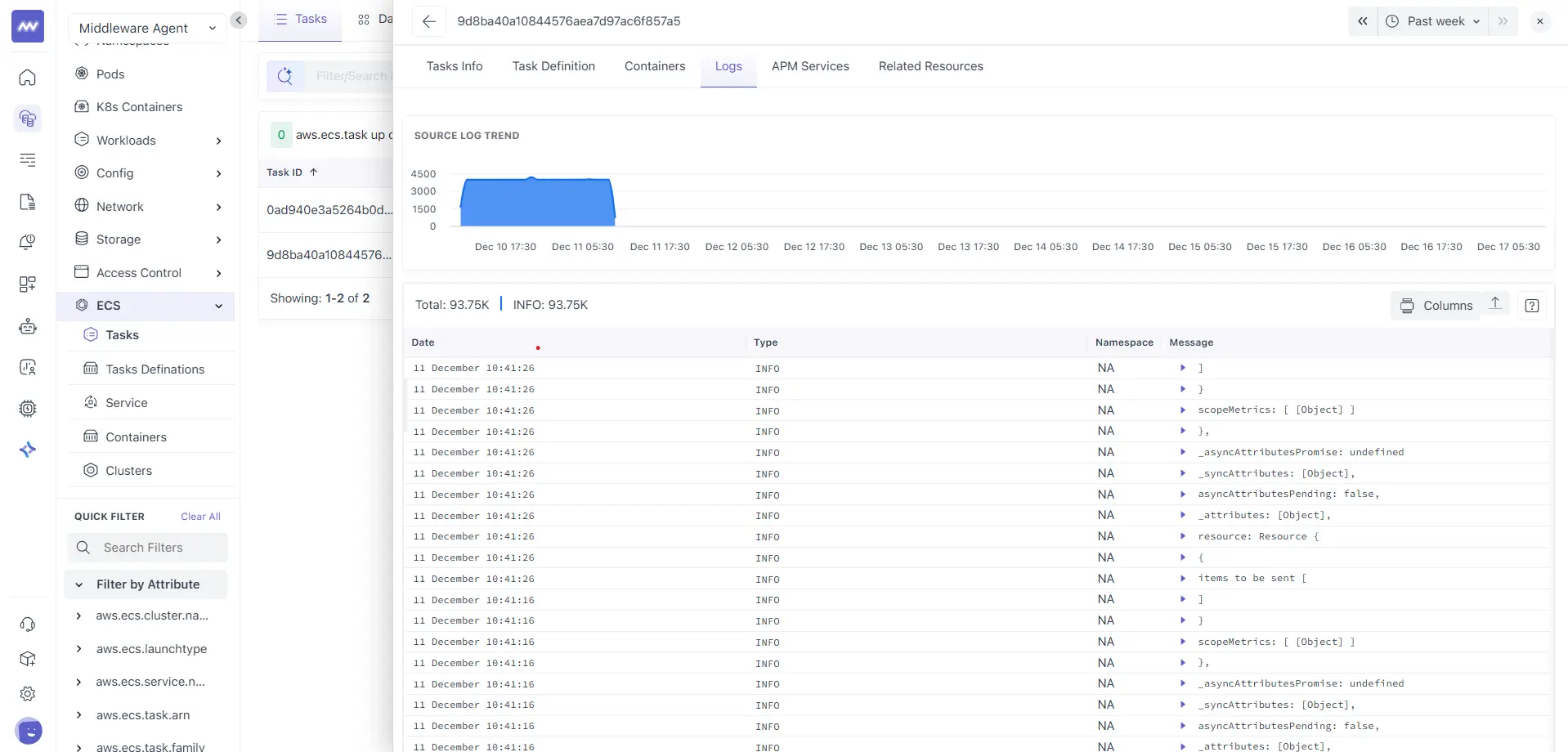
The Logs tab on the task provides aggregated logs for all containers within the task and shows you:
- Source log trend chart for log volume over time
- Total log count and level breakdown
- A log table with fields such as Date, Type, Namespace, and Message
- A Columns control to adjust visible fields
Use this view when the issue is task-scoped, and you want a combined log stream for the entire task.
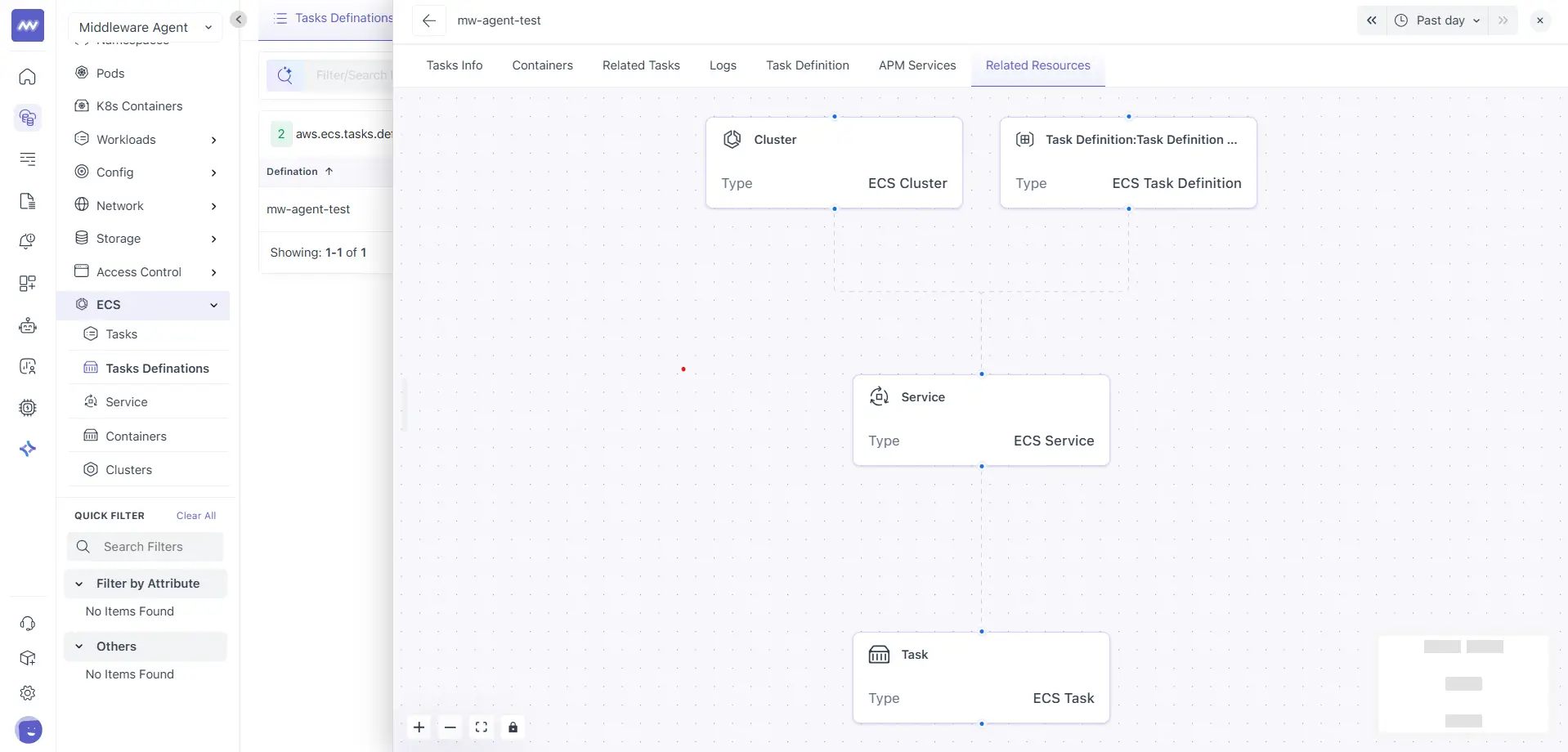
Related Resources
The Related Resources tab shows a relationship graph for the selected task.
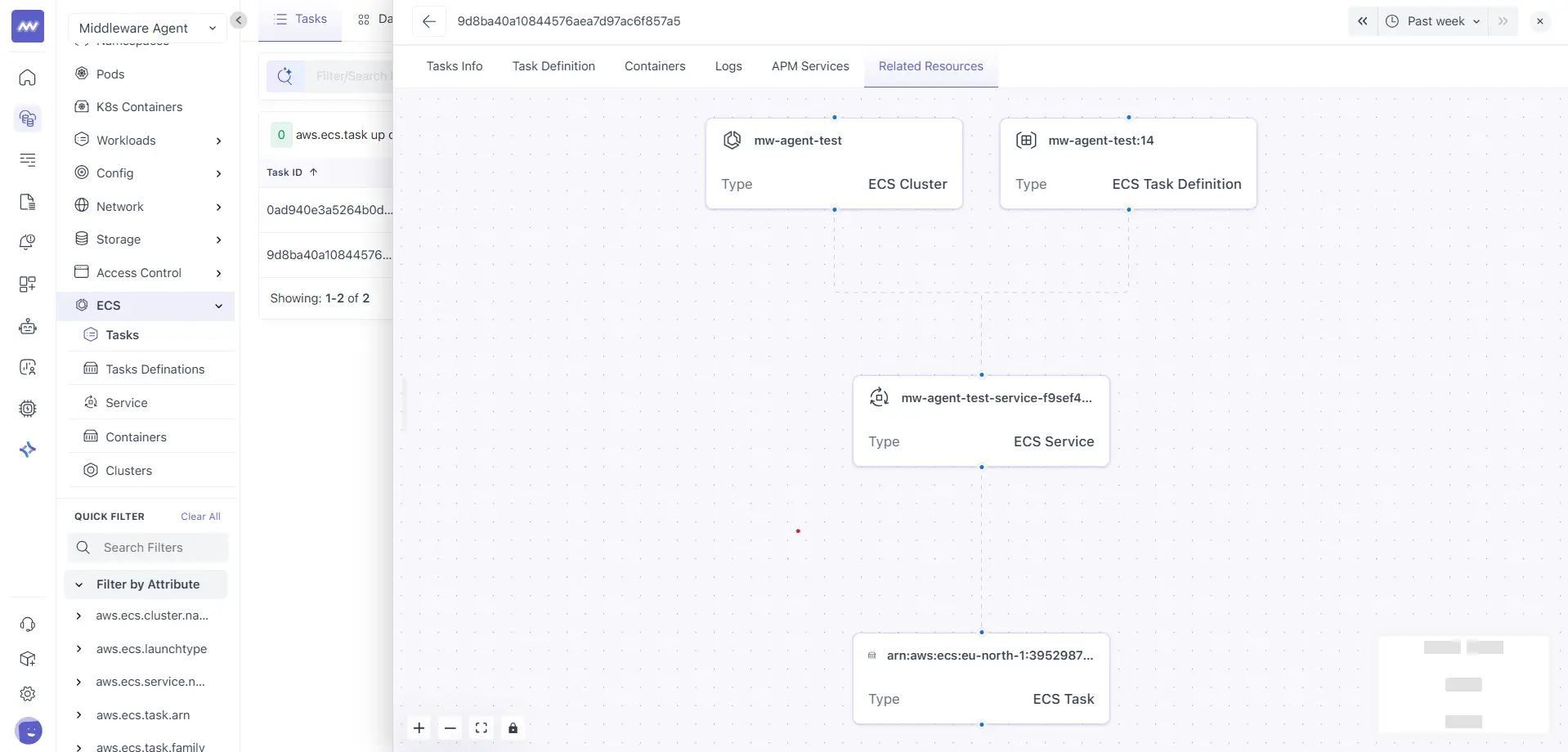
A visual view of linked ECS entities, typically including:
- ECS Cluster
- ECS Task Definition
- ECS Service
- ECS Task
Use this view to understand how the task fits into the broader ECS structure and to quickly jump to the parent service, task definition, or cluster.
Tasks Definitions
The Tasks Definitions section provides visibility into ECS task definition configurations and how they are used by running tasks. This view helps you understand how workloads are defined and how configuration changes relate to runtime behaviour.
A task definition acts as the blueprint for ECS tasks. It defines container images, resource limits, networking settings, environment variables, and runtime permissions.
Tasks Definitions list
The Tasks Definitions list shows all task definitions detected in your ECS environment for the selected time range.
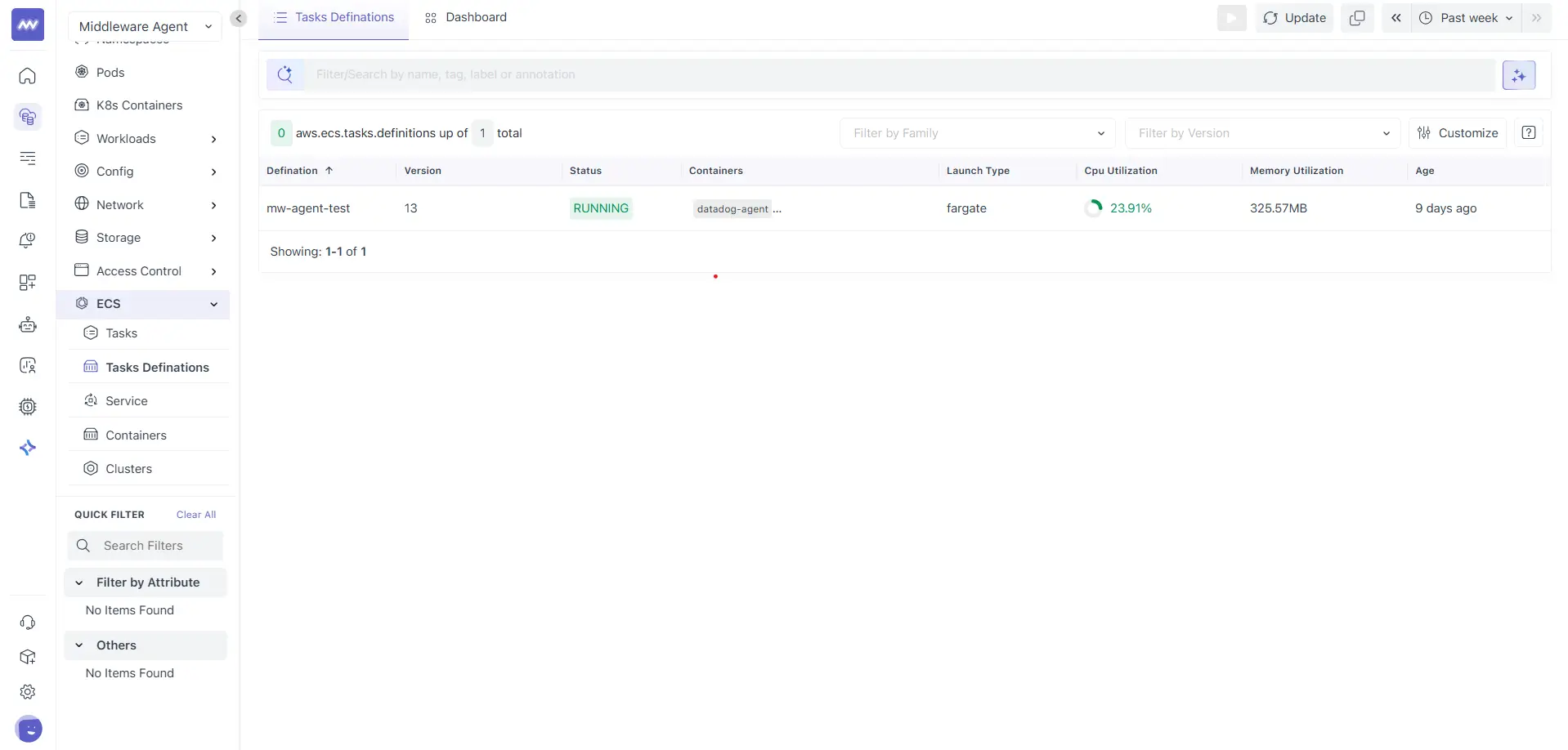
Here, each row represents a task definition family and revision. Common columns include:
- Definition: Task definition family name
- Version: Task definition revision
- Status: Current status of tasks created from this definition
- Containers: Container names defined in the task definition
- Launch Type: Launch type used by tasks created from this definition
- CPU Utilization: Aggregated CPU usage across related tasks
- Memory Utilization: Aggregated memory usage across related tasks
- Age: Time since the task definition was observed
Tasks Info
The Tasks Info tab provides a summary of the selected task definition and high-level configuration details.
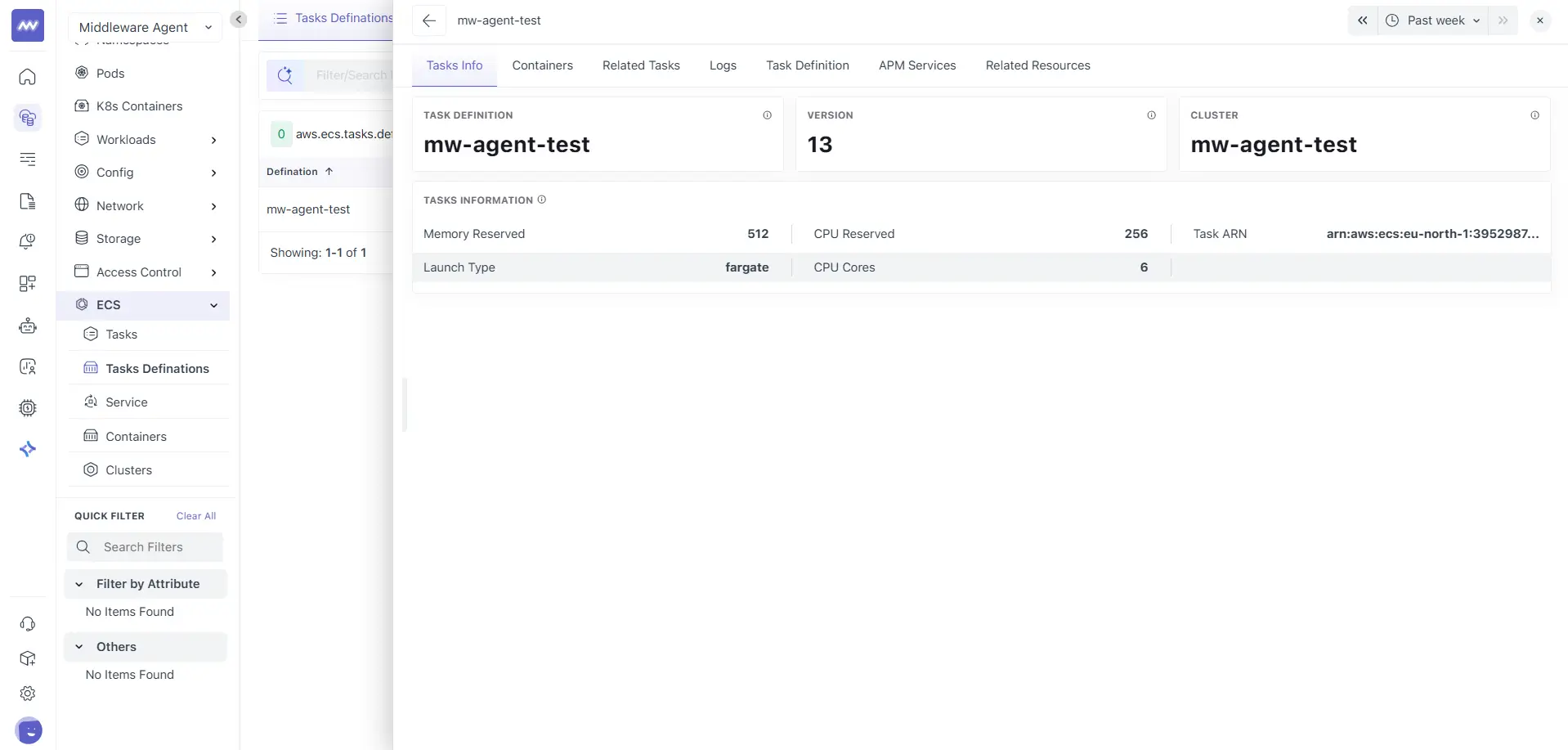
This section displays:
- Task Definition name
- Version
- Cluster
These values help you confirm where the task definition is actively used.
Task definition information The information panel includes:
- Memory reserved
- CPU reserved
- Launch type
- CPU cores
- Task ARN
This view is useful when validating resource configuration before investigating runtime issues.
Containers
The Containers tab lists all containers defined in the selected task definition.
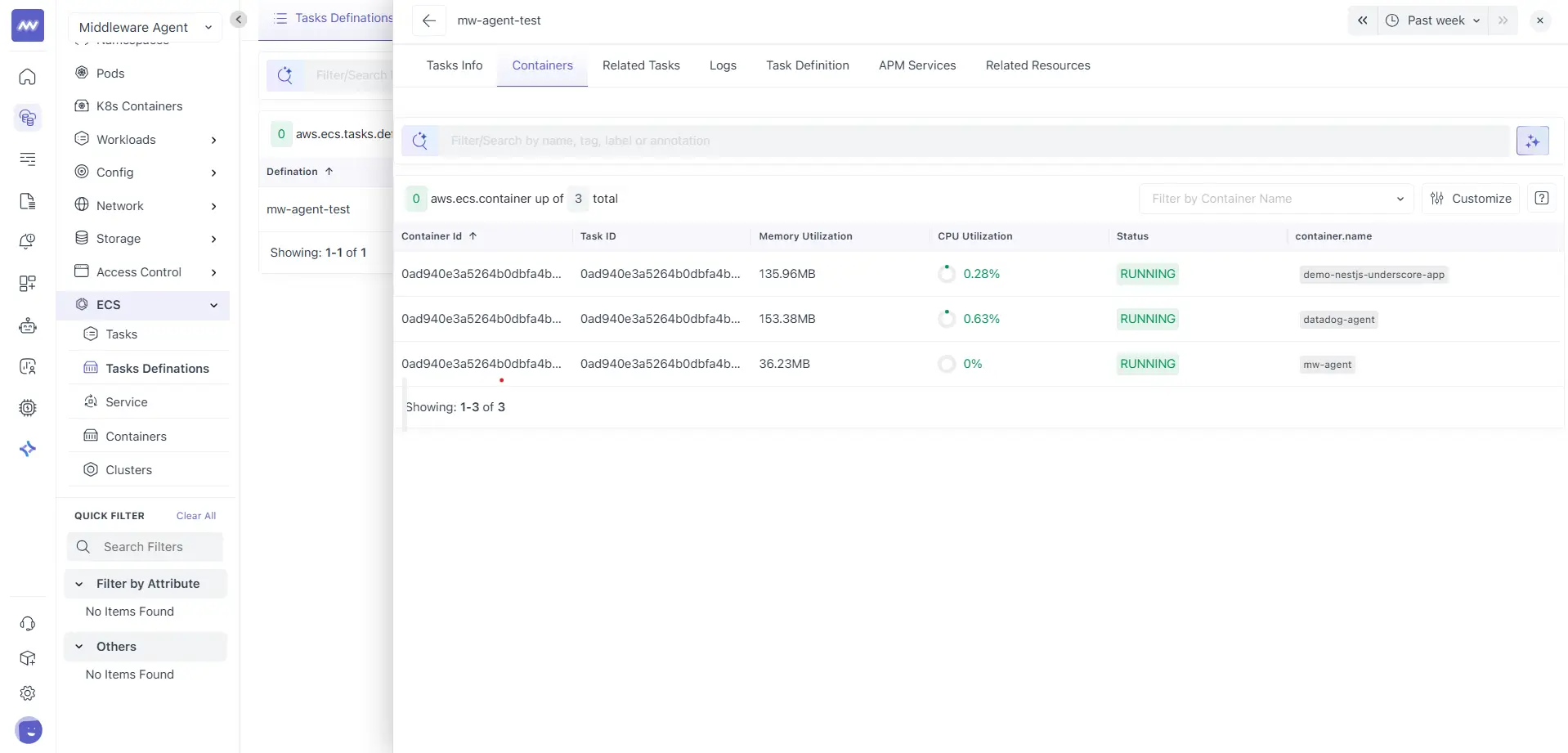
Each row represents a container defined in the task definition. Common columns include:
- Container ID
- Task ID
- Memory utilization
- CPU utilization
- Status
- container.name
This view helps you confirm container composition and resource behaviour across tasks created from the same definition.
Container drilldowns behave the same way as in the Tasks page and provide container-level metrics and logs.
Related Tasks
The Related Tasks tab lists all ECS tasks created from the selected task definition.
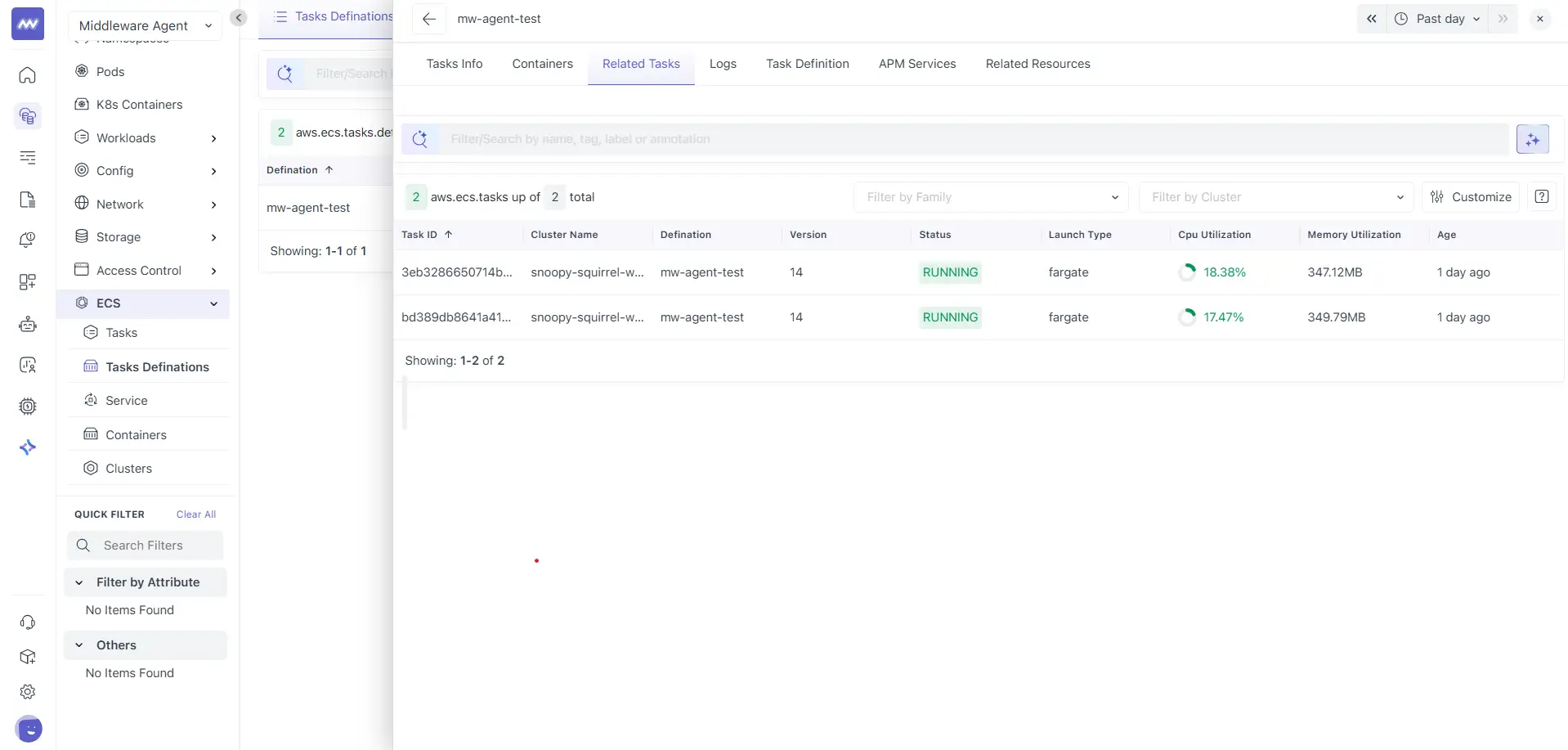
This table is identical in structure and behaviour to the Tasks list view. It includes:
- Task ID
- Cluster name
- Definition
- Version
- Status
- Launch type
- CPU utilization
- Memory utilization
- Age
Clicking a task opens the task details view, which behaves exactly the same as the Tasks page described earlier:
Use this view to compare how different tasks created from the same definition behave at runtime.
Logs
The Logs tab shows aggregated logs from all tasks created using the selected task definition.
- A source log trend showing log volume over time
- Total log count and level breakdown
- A log table with fields such as Date, Type, Namespace, and Message
- A Columns control to adjust visible fields
This view is useful when validating deployments or investigating issues that affect all tasks created from a specific definition.
Task Definition
The Task Definition tab displays the full task definition configuration and shows you the following:
- A YAML view of the task definition
- A tags panel that helps navigate configuration sections
With task definitions, you can perform the following actions:
- View Version allows you to switch between task definition revisions
- Compare Version helps review changes between versions
- The timestamp selector allows viewing the configuration captured at a specific time
- The download option allows exporting the task definition
This tab is commonly used during deployment reviews or when correlating configuration changes with runtime behaviour.
APM Services
The APM Services tab shows application services associated with tasks created from this task definition.
This view helps correlate task definition level changes with application performance and traces.
Related Resources
The Related Resources tab shows a relationship graph for the selected task definition.

The graph typically includes:
- ECS Cluster
- ECS Task Definition
- ECS Service
- ECS Tasks
This view helps you understand how the task definition fits into the broader ECS structure and allows quick navigation to related services, tasks, and clusters.
Great, this fits very cleanly into the flow you have built so far. Below is the Service documentation written to match the Tasks and Tasks Definitions sections exactly.
It follows all your guidelines:
- Simplified, descriptive, professional tone
- No em dashes
- No semicolons
- Consistent wording and structure
- Explicit callout where behaviour is the same as earlier pages
- Aligned to the screenshots you shared in sequence
Service
The Service section provides visibility into ECS services that manage long-running workloads. This view helps you understand service level stability, task management behaviour, resource usage, logs, and application performance.
An ECS service ensures that a specified number of tasks remain running. If a task stops or fails, the service replaces it automatically based on the configured task definition.
Service List
The Service list shows all ECS services detected in your environment for the selected time range.
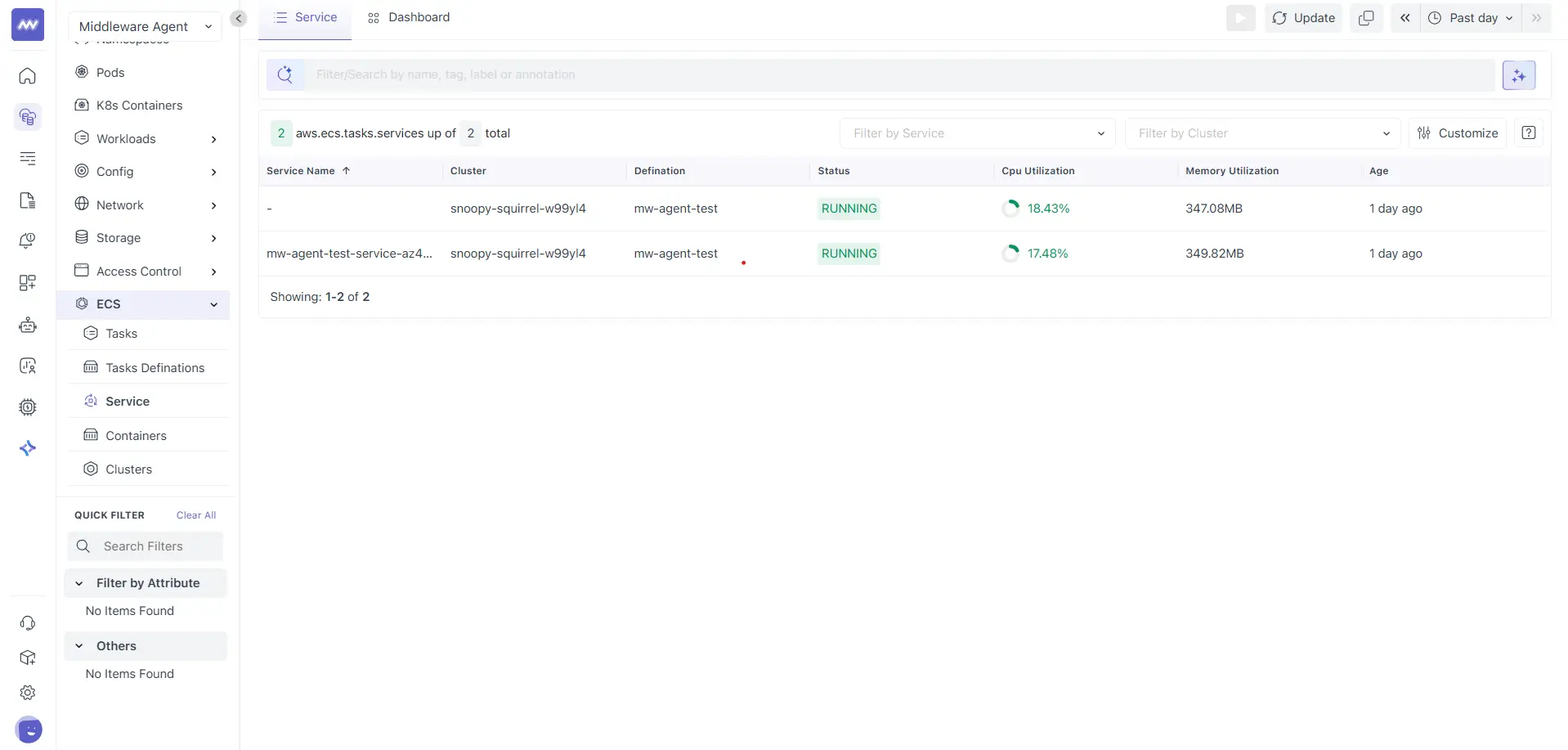
Here, each row represents an ECS service. Common columns include:
- Service Name: Name of the ECS service
- Cluster: ECS cluster where the service is running
- Definition: Task definition used by the service
- Status: Current service state
- CPU Utilization: Aggregated CPU usage across tasks managed by the service
- Memory Utilization: Aggregated memory usage across tasks
- Age: Time since the service was observed
Click a service name to open the service details view.
Service Info
The Service Info tab provides a high-level overview of the selected ECS service.
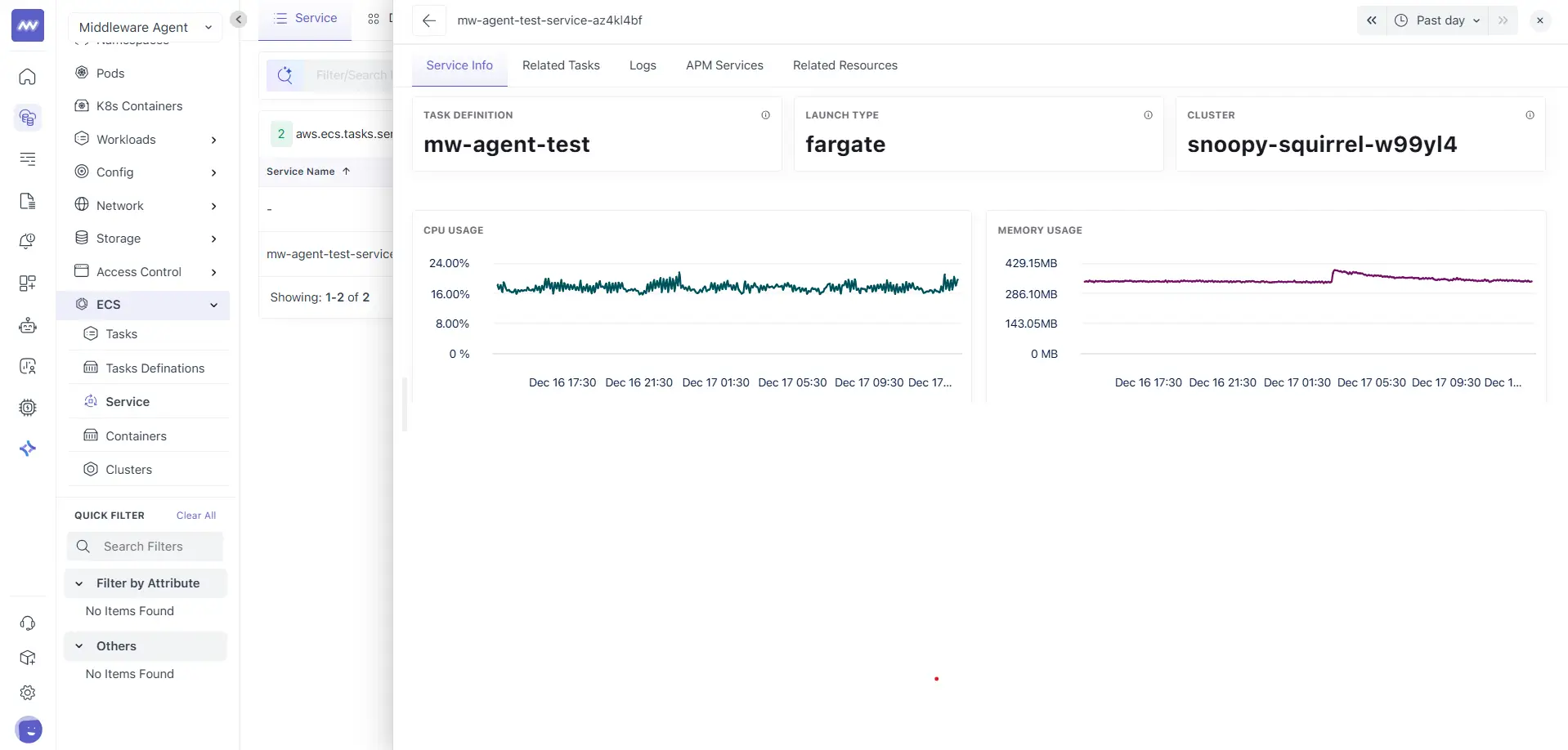
This section displays:
- Task Definition used by the service
- Launch Type
- Cluster
These values help you confirm how and where the service is running.
On the other hand, there is a performance tab which includes service level charts, such as:
- CPU usage
- Memory usage
These charts reflect aggregated behaviour across all tasks managed by the service and help identify sustained load or abnormal patterns.
Related Tasks
The Related Tasks tab lists all ECS tasks currently managed by the selected service.
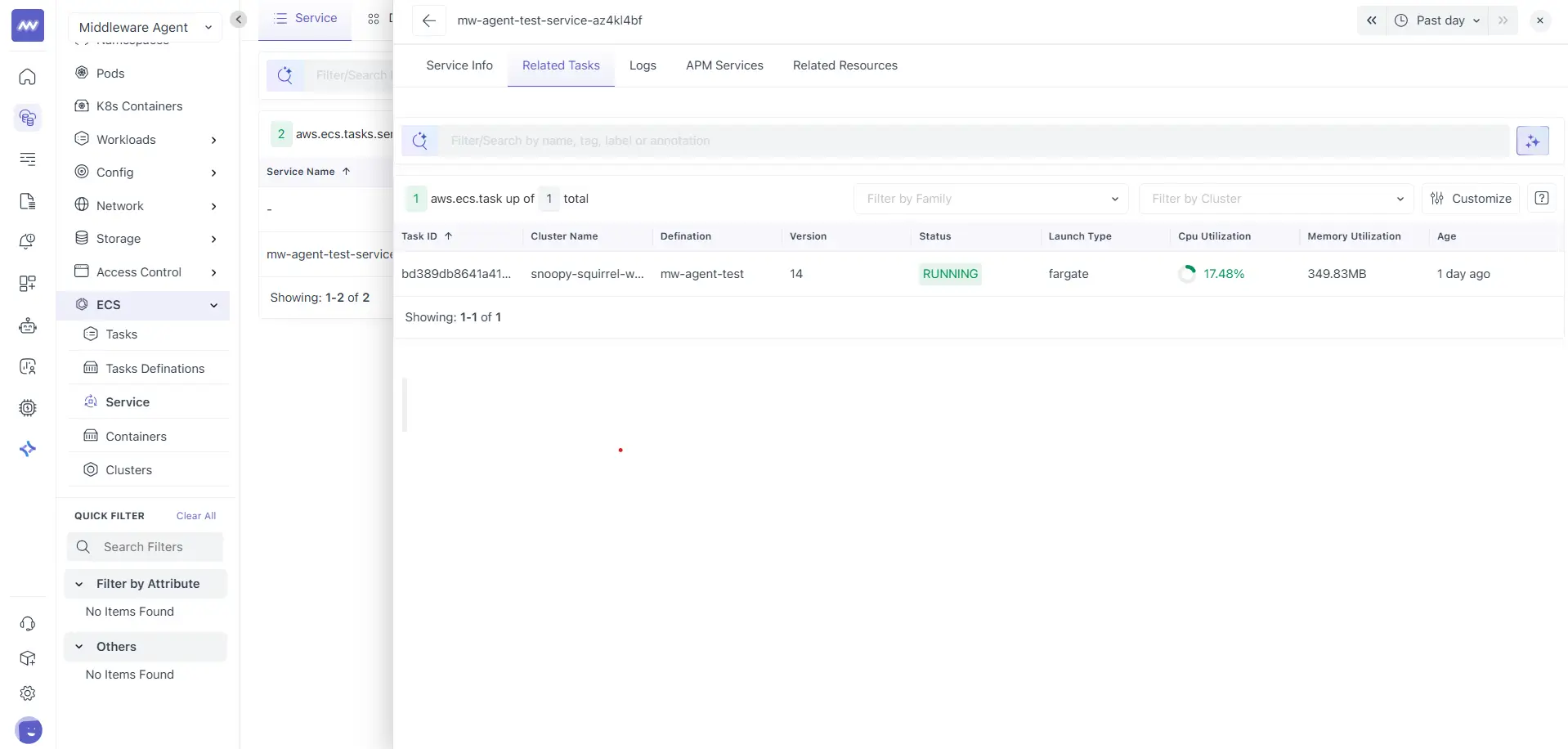
This table is identical in structure and behaviour to the Tasks list view and includes:
- Task ID
- Cluster name
- Definition
- Version
- Status
- Launch type
- CPU utilization
- Memory utilization
- Age
Clicking a task opens the same task details view described in the Tasks section earlier.

All tabs and behaviour remain unchanged, including:
- Tasks Info
- Task Definition
- Containers
- Logs
- APM Services
- Related Resources
This consistency allows you to move from service level context directly into task level investigation without learning a new workflow.
Logs
The Logs tab shows aggregated logs from all tasks running under the selected service.
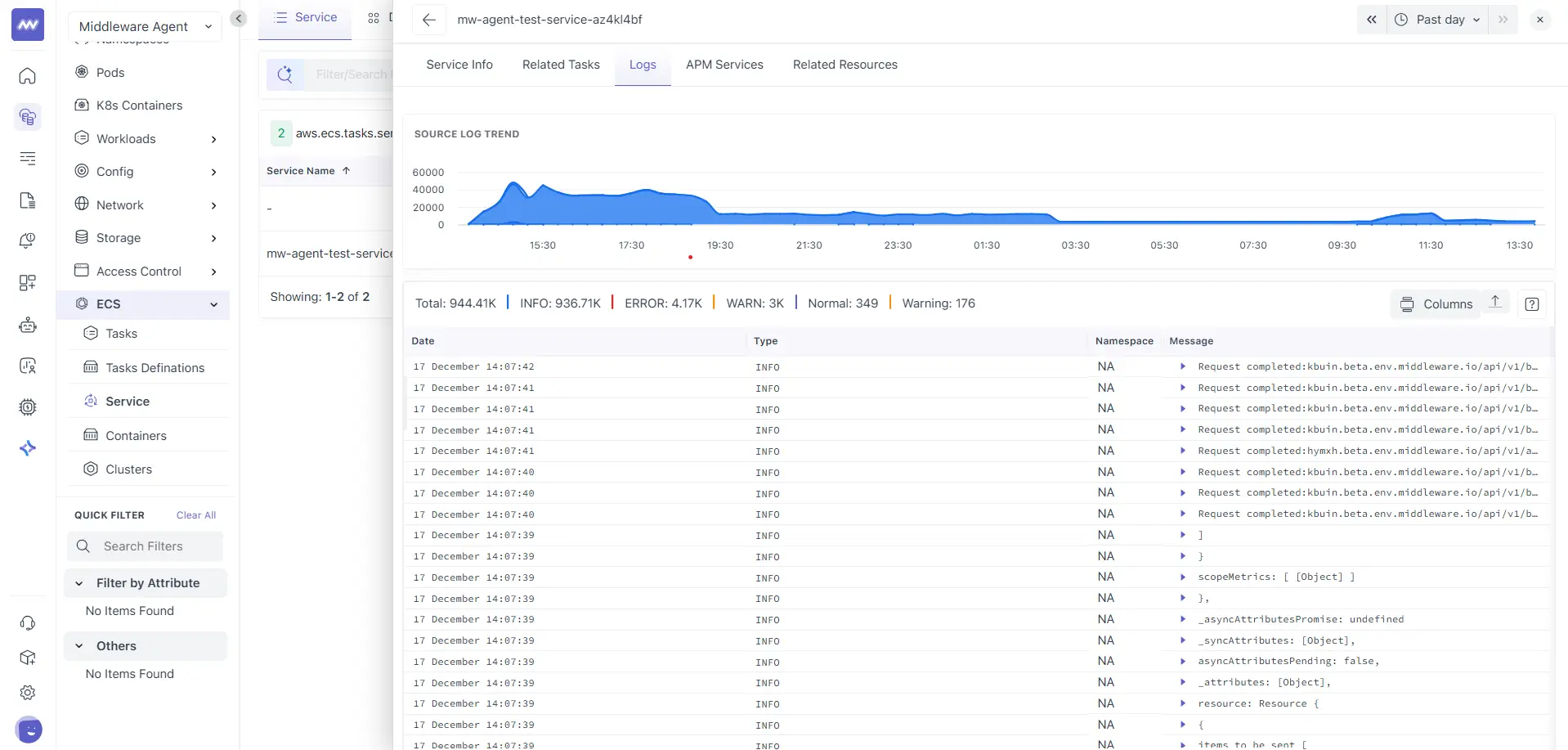
It shows:
- A source log trend chart showing log volume over time
- Total log count with level breakdown
- A logs table with fields such as Date, Type, Namespace, and Message
- A Columns option to adjust visible fields
This view is useful when diagnosing issues that affect the service as a whole rather than a single task.
APM Services
The APM Services tab displays application services associated with workloads managed by the ECS service.
This view helps correlate service level infrastructure behaviour with application performance, traces, and errors.
Related Resources
The Related Resources tab shows a relationship graph for the selected ECS service.

The graph typically includes:
- ECS Cluster
- ECS Task Definition
- ECS Service
- ECS Tasks
This view helps you understand how the service fits into the ECS hierarchy and allows quick navigation to related entities.
Containers
The Containers section provides container level visibility for workloads running inside ECS tasks. This view helps you inspect the most granular execution unit where application processes run and where logs and resource usage originate.
Use this section when you want to understand container health, resource consumption, and logs for a specific container instance.
The first page lists all ECS containers detected in your environment for the selected time range:
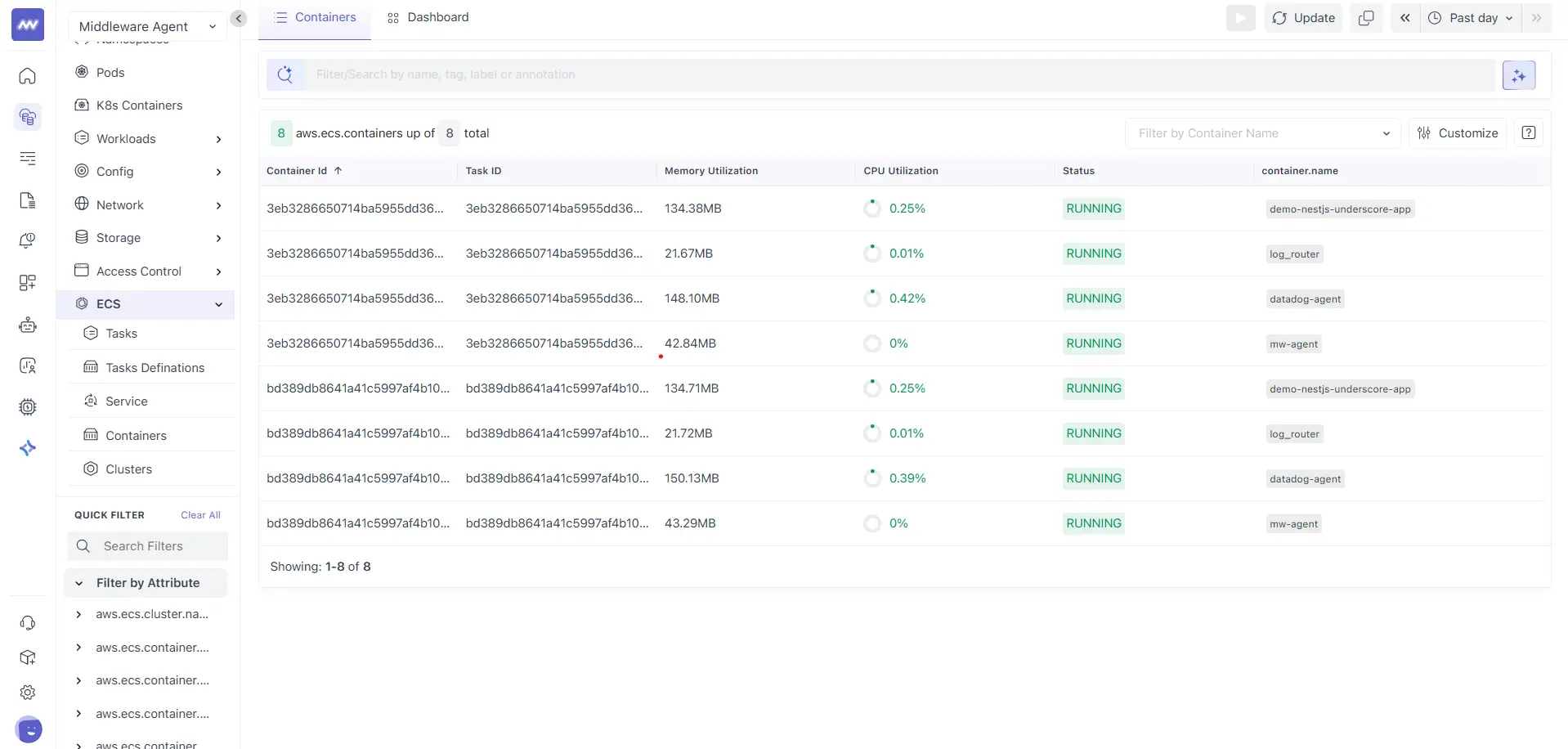
Here, each row represents a running container instance. Common columns include:
- Container ID: Unique identifier for the container
- Task ID: ECS task where the container is running
- Memory Utilization: Current memory usage of the container
- CPU Utilization: Current CPU usage of the container
- Status: Runtime status of the container
- container.name: Container name defined in the task definition
Container Info
The Container Info tab provides a detailed overview of the selected container.
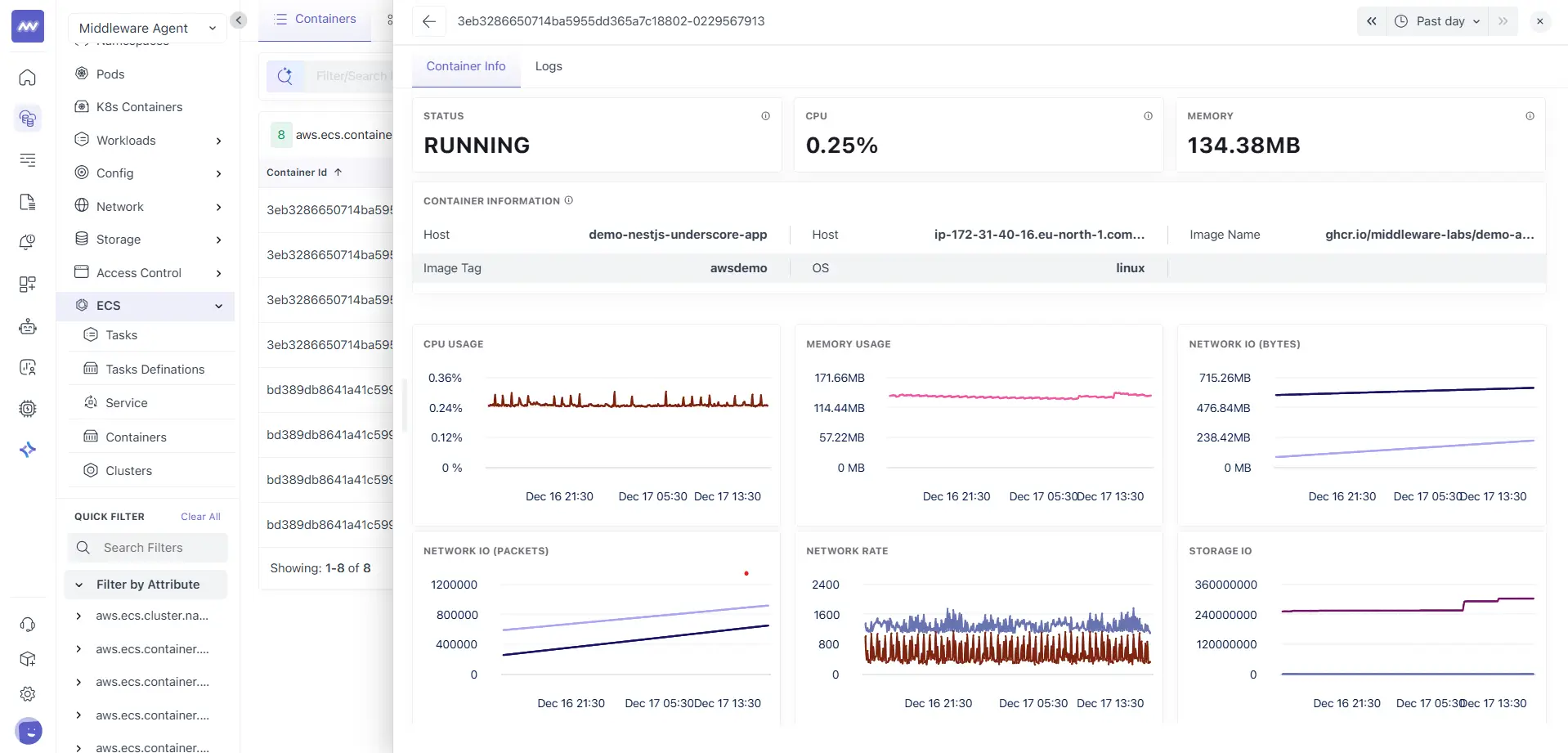
Summary cards
This section shows:
- Status
- CPU
- Memory
These values help you quickly confirm whether the container is healthy and actively consuming resources.
Container information
The container information panel includes metadata such as:
- Host
- Image name
- Image tag
- Operating system
This information helps validate container identity and runtime environment.
Performance charts
The Container Info view includes time series charts for:
- CPU usage
- Memory usage
- Network IO in bytes
- Network IO in packets
- Network rate
- Storage IO
Use these charts to identify spikes, sustained usage patterns, or abnormal behaviour at the container level.
Logs
The Logs tab shows logs generated by the selected container.

It shows the following:
- A source log trend chart showing log volume over time
- Total log count and level breakdown
- A log table with fields such as Date, Type, Namespace, and Message
- A Columns option to adjust visible fields
This view is useful when debugging container-specific issues or investigating application-level errors emitted by a single container.
Perfect. Below is the Clusters section documentation, written to stay fully consistent with Tasks, Task Definitions, Service, and Containers.
This follows all your guidelines:
- Simplified, descriptive, professional tone
- No em dashes
- No semicolons
- Same structure and phrasing style
- Explicitly mentions shared behaviour where screens are reused
- Aligned with the screenshots you shared in order
Clusters
The Clusters section provides a high-level view of ECS clusters where tasks and services run. This view helps you understand overall resource usage, workload distribution, and cluster-level activity.
Use this section to monitor cluster health, capacity usage, and drill down into tasks running inside a cluster.
Clusters list
The Clusters list shows all ECS clusters detected in your environment for the selected time range.
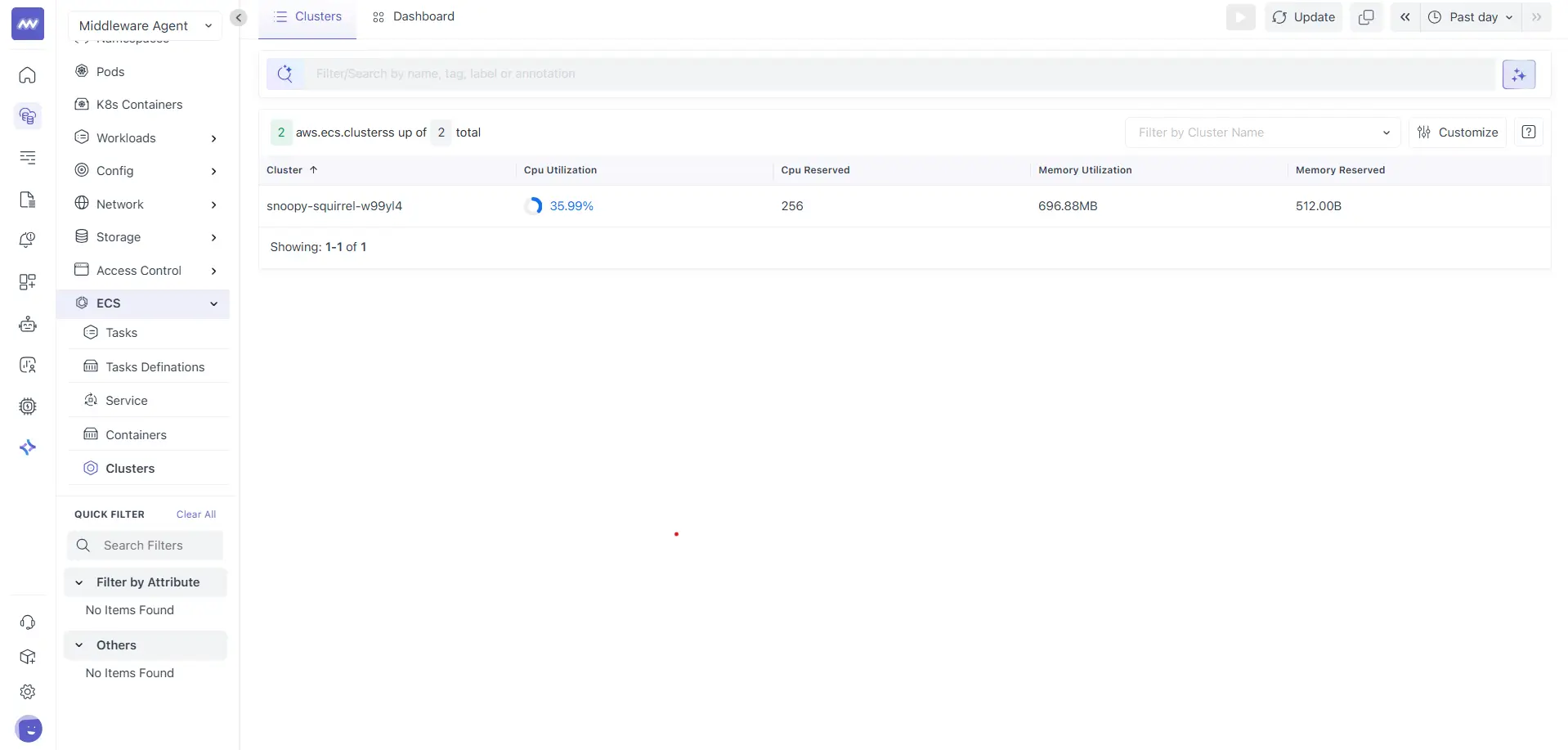
Each row represents an ECS cluster. Common columns include:
- Cluster: Name of the ECS cluster
- CPU Utilization: Aggregated CPU usage across tasks running in the cluster
- CPU Reserved: CPU reserved by tasks in the cluster
- Memory Utilization: Aggregated memory usage
- Memory Reserved: Memory reserved by tasks
Click a cluster name to open the cluster details view.
Cluster Info
The Cluster Info tab provides an overview of the selected ECS cluster.
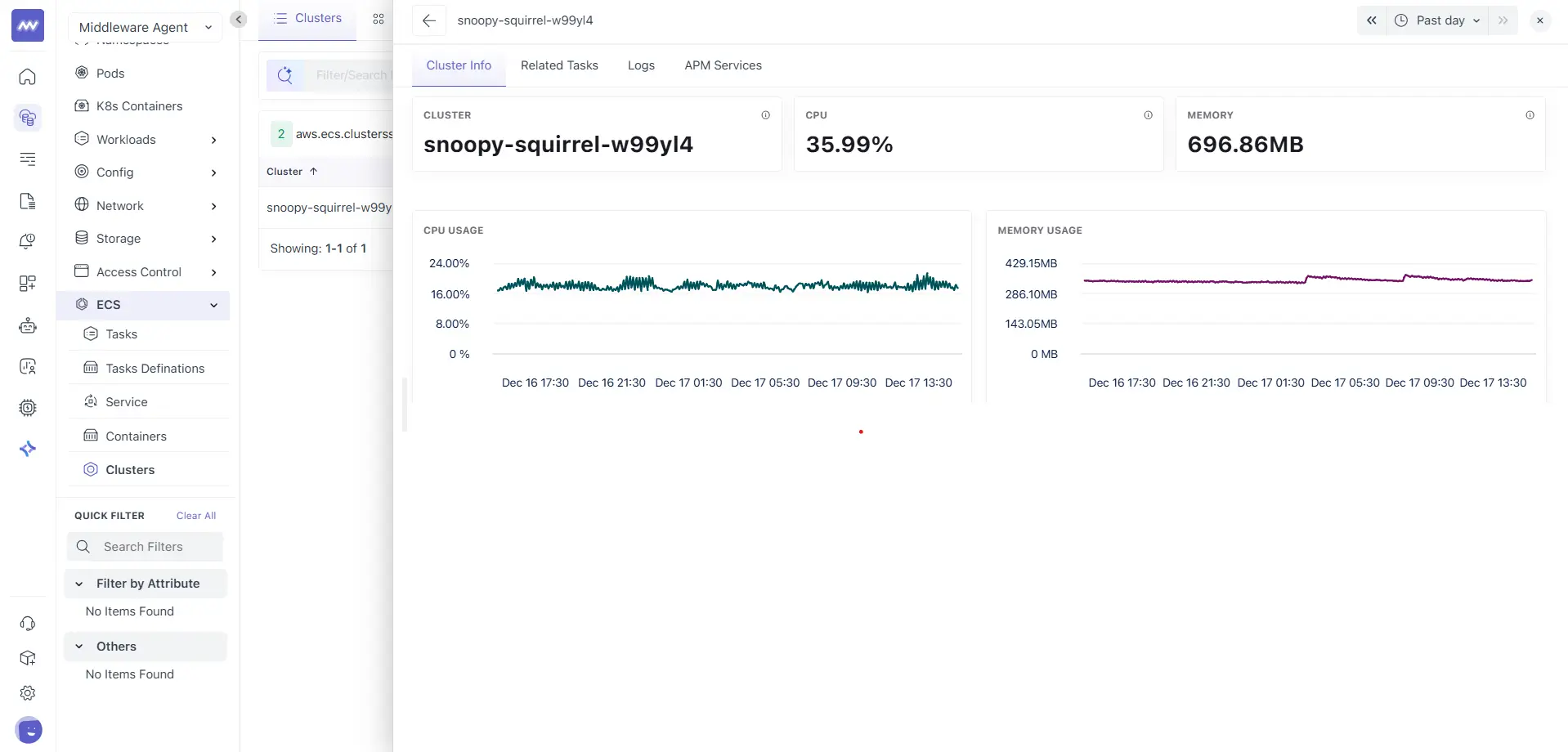
Summary cards
This section shows:
- Cluster name
- CPU utilization
- Memory utilization
These values help you quickly assess overall cluster load.
Performance Charts
This tab includes cluster-level charts, such as:
- CPU usage over time
- Memory usage over time
These charts represent aggregated behaviour across all tasks running in the cluster and are useful for capacity planning and trend analysis.
Related Tasks
The Related Tasks tab lists all ECS tasks running inside the selected cluster.
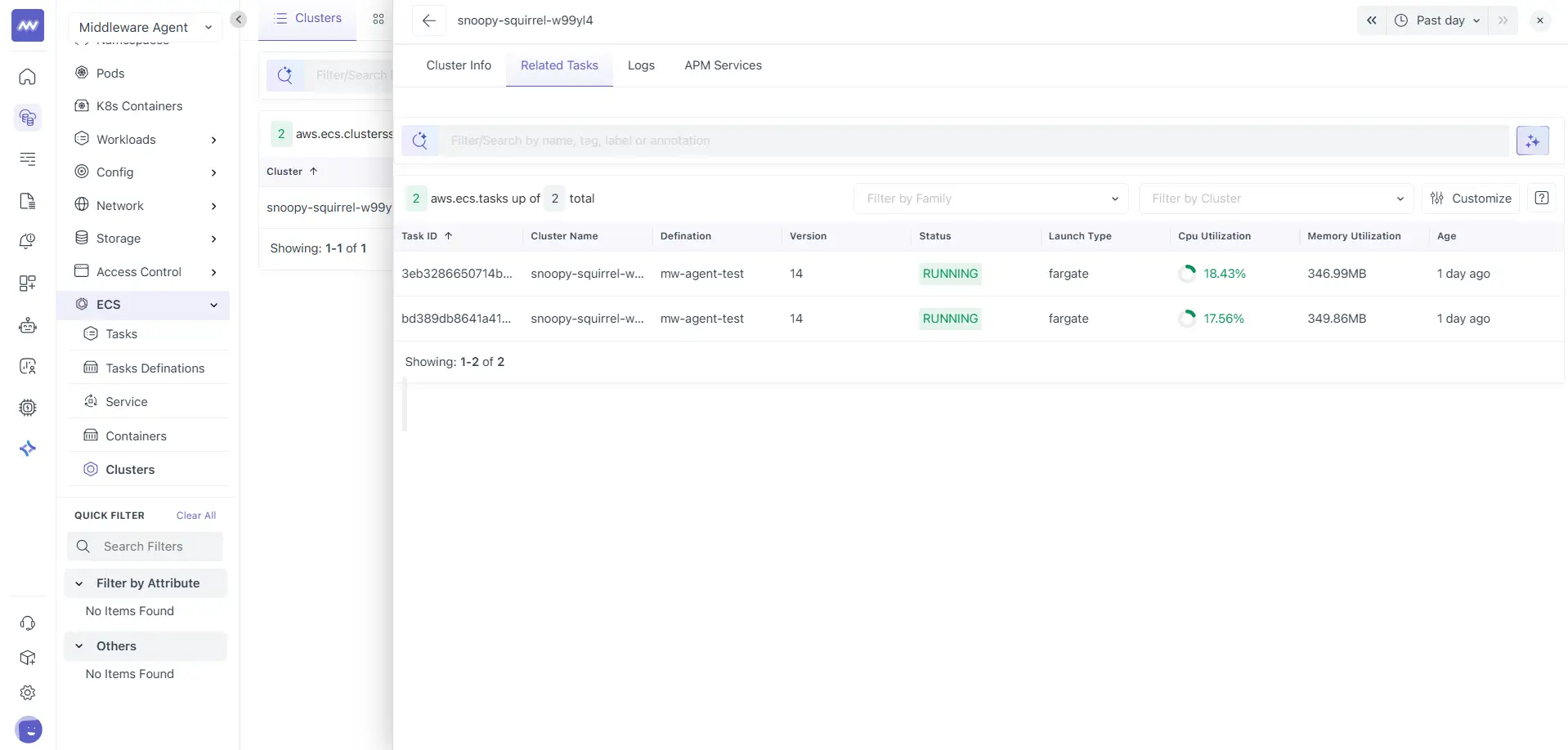
This table is identical in structure and behaviour to the Tasks list view and includes:
- Task ID
- Cluster name
- Definition
- Version
- Status
- Launch type
- CPU utilization
- Memory utilization
- Age
Task drilldown behaviour
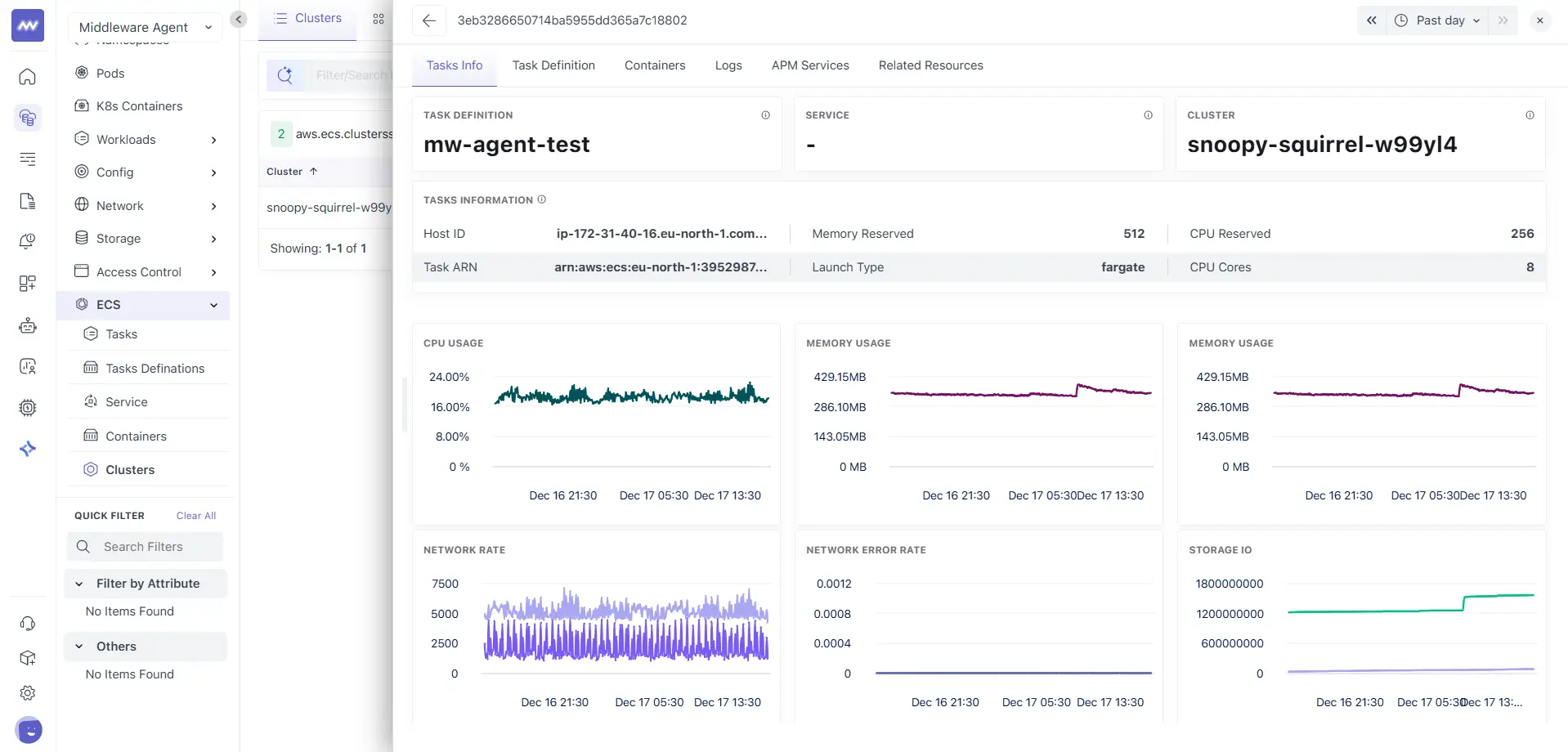
Clicking a task opens the same task details view described earlier in the Tasks section. All tabs and behaviour remain unchanged, including:
- Tasks Info
- Task Definition
- Containers
- Logs
- APM Services
- Related Resources
This allows seamless navigation from cluster-level context to task-level investigation.
Logs
The Logs tab shows aggregated logs generated by all tasks and containers running in the selected cluster.
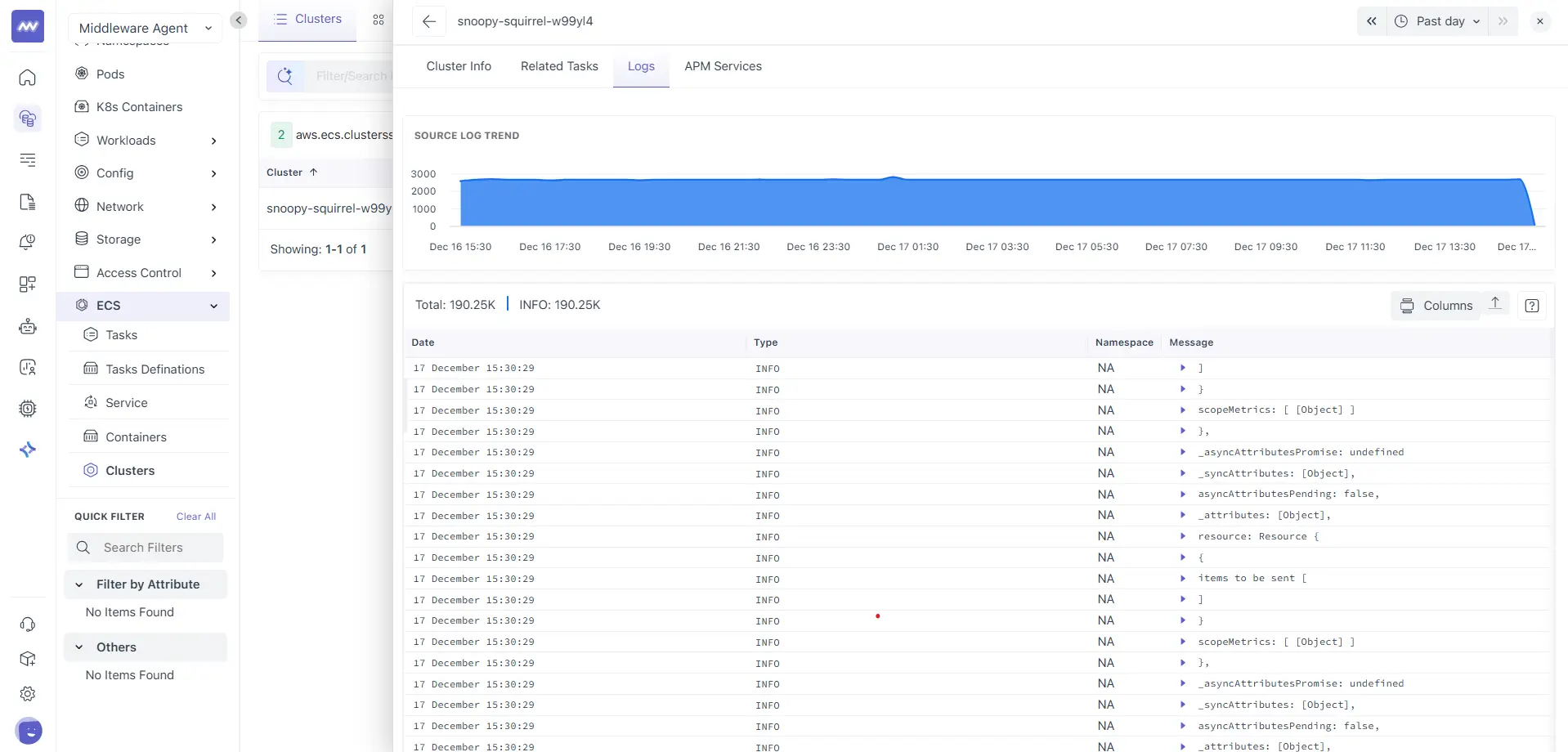
It shows:
- A source log trend chart showing log volume over time
- Total log count with level breakdown
- A log table with fields such as Date, Type, Namespace, and Message
- A Columns option to control visible fields
This view is useful for identifying cluster-wide issues or increased log activity across workloads.
APM Services
The APM Services tab displays application services associated with workloads running inside the cluster.
This view helps correlate cluster-level resource behaviour with application performance and errors.
How Clusters relate to other ECS resources
Clusters act as the execution boundary for ECS workloads. From a cluster, you can navigate to:
- ECS tasks running in the cluster
- ECS services managing those tasks
- Task definitions used to create the tasks
- Containers running inside the tasks
This relationship allows you to move from infrastructure level context to workload level details without leaving the ECS section.
Need assistance or want to learn more about Middleware? Contact our support team at [email protected] or join our Slack channel.