Amazon ECS
Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a fully managed container orchestration service that helps you easily deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications.
With the Middleware Agent (MW Agent), you can effectively monitor your ECS containers and tasks running on every EC2 instance in your cluster as well as on ECS Fargate.
Database Integrations and the Amazon ECS Anywhere approach are not currently supported.
Fargate Setup
Use the Middleware and AWS Fargate integration to monitor your applications without having to manage servers. This involves creating or updating a task definition to have the following three container definitions:
- Primary application Container: Hosts the main application that emits telemetry.
- Middleware Agent Container: Collects, processes, and exports telemetry data.
- Fluent Bit Container: Routes logs from the primary application container and forwards them to your Middleware account.
Create the Middleware Agent Container
Although the following example uses environment variables, it is recommended to use AWS Secrets to store your MW_API_KEY and MW_TARGET values.
For Each ECS Task that you want to monitor, add the following sidecar container to your containerDefinitions array.
{
"name": "mw-agent",
"image": "ghcr.io/middleware-labs/mw-host-agent:master",
"cpu": 256,
"portMappings": [
{
"name": "8006-tcp",
"containerPort": 8006,
"hostPort": 8006,
"protocol": "tcp",
"appProtocol": "http"
}
],
"essential": true,
"environment": [
{
"name": "MW_API_KEY",
"value": "<MW_API_KEY>"
},
{
"name": "MW_TARGET",
"value": "https://<MW_UID>.middleware.io:443"
},
],
"mountPoints": [],
"volumesFrom": [],
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awslogs",
"options": {
"awslogs-group": "<YOUR_LOGS_GROUP>",
"mode": "non-blocking",
"awslogs-create-group": "true",
"max-buffer-size": "25m",
"awslogs-region": "<YOUR_REGION>",
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "ecs"
}
}
}Collect Metrics
Adding the sidecar container mentioned above will automatically collect metrics data from your ECS tasks and containers. The MW Agent uses the AWS ECS Task Metadata Endpoint to fetch metrics data.
Collect Task Logs
The mw-agent sidecar, mentioned above, must be running before proceeeding.
Forward your ECS Task logs to your Middleware account by creating a Fluent Bit sidecar container and configuring FireLens.
Step 1: Add a Fluent Bit Container in Your ECS task
Add the following sidecar container to your containerDefinitions array
JSON
{
"name": "log_router",
"image": "amazon/aws-for-fluent-bit:stable",
"cpu": 0,
"portMappings": [],
"essential": true,
"environment": [],
"mountPoints": [],
"volumesFrom": [],
"user": "0",
"firelensConfiguration": {
"type": "fluentbit",
"options": {
"enable-ecs-log-metadata": "true"
}
}
}Step 2: Add a Log Configuration in Your Primary Application Container
The MW Agent sidecar will fetch these logs and send them to Middleware.
JSON
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awsfirelens",
"options": {
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
"Name": "forward",
"Port": "8006"
}
}Parsing JSON Structured Logs [Optional]
Firelens by default sends a JSON blob which Middleware displays as the log body. Parsing the JSON logs allows the Message of the log being displayed while the attributes will be viewable on expansion.
To change the behavior you will need to add the below options to the firelensConfiguration created in Step 1.
The JSON structured logs generated need to have a Message field. Otherwise Middleware will not know what should be shown as a body of the log.
JSON
"firelensConfiguration": {
"type": "fluentbit",
"options": {
"enable-ecs-log-metadata": "true",
"config-file-type": "file",
"config-file-value": "/fluent-bit/configs/parse-json.conf"
}
}Complete Example
Although the following example uses environment variables, it is recommended to use AWS Secrets to store your MW_API_KEY and MW_TARGET values.
{
"family": ...,
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "your-primary-application-container",
...
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awsfirelens",
"options": {
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
"Name": "forward",
"Port": "8006"
}
}
},
{
"name": "mw-agent",
"image": "ghcr.io/middleware-labs/mw-host-agent:master",
"cpu": 256,
"portMappings": [
{
"name": "8006-tcp",
"containerPort": 8006,
"hostPort": 8006,
"protocol": "tcp",
"appProtocol": "http"
}
],
"essential": true,
"environment": [
{
"name": "MW_TARGET",
"value": "https://<MW_UID>.middleware.io:443"
},
{
"name": "MW_API_KEY",
"value": "<MW_API_KEY>"
}
],
"mountPoints": [],
"volumesFrom": [],
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awslogs",
"options": {
"awslogs-group": "<YOUR_LOGS_GROUP>",
"mode": "non-blocking",
"awslogs-create-group": "true",
"max-buffer-size": "25m",
"awslogs-region": "<YOUR_REGION>",
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "ecs"
}
},
"systemControls": []
},
{
"name": "log_router",
"image": "amazon/aws-for-fluent-bit:stable",
"cpu": 0,
"portMappings": [],
"essential": true,
"environment": [],
"mountPoints": [],
"volumesFrom": [],
"user": "0",
"systemControls": [],
"firelensConfiguration": {
"type": "fluentbit",
"options": {
"enable-ecs-log-metadata": "true",
"config-file-type": "file",
"config-file-value": "/fluent-bit/configs/parse-json.conf"
}
}
}
],
...
}EC2 Setup
Step 1: Create & Configure a MW Agent ECS Task Definition
Begin by creating a Task Definition for the MW Agent container.
Select appropriate tab below depending on the network mode desired for the MW Agent
Host Network Mode
{
"family": "mw-agent-task",
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "mw-agent",
"image": "ghcr.io/middleware-labs/mw-host-agent:master",
"cpu": 100,
"memory": 512,
"portMappings": [
{
"name": "mw-agent-9319-tcp",
"containerPort": 9319,
"hostPort": 9319,
"protocol": "tcp",
"appProtocol": "grpc"
},
{
"name": "mw-agent-8006-tcp",
"containerPort": 8006,
"hostPort": 8006,
"protocol": "tcp"
},
{
"name": "mw-agent-9320-tcp",
"containerPort": 9320,
"hostPort": 9320,
"protocol": "tcp"
}
],
"essential": true,
"environment": [
{
"name": "MW_API_KEY",
"value": "<Your MW API Key here>"
},
{
"name": "MW_TARGET",
"value": "<Your MW Target here>"
}
],
"mountPoints": [
{
"sourceVolume": "docker-sock",
"containerPath": "/var/run/docker.sock",
"readOnly": false
},
{
"sourceVolume": "proc",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/proc",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "dev",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/dev",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al2_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/sys/fs/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al1_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al2_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/sys/fs/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al1_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "docker-containers-root",
"containerPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "var-log-host",
"containerPath": "/var/log",
"readOnly": true
}
],
"volumesFrom": [],
"privileged": true,
"systemControls": []
}
],
"networkMode": "host",
"volumes": [
{
"name": "docker-sock",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/var/run/docker.sock"
}
},
{
"name": "proc",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/proc"
}
},
{
"name": "dev",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/dev"
}
},
{
"name": "al1_cgroup",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/cgroup"
}
},
{
"name": "al2_cgroup",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/sys/fs/cgroup"
}
},
{
"name": "docker-containers-root",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/var/lib/docker/containers"
}
},
{
"name": "var-log-host",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/var/log"
}
}
],
"requiresCompatibilities": [
"EC2"
],
"pidMode": "host"
}Bridge (Default) Network Mode
{
"family": "mw-agent-task",
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "mw-agent",
"image": "ghcr.io/middleware-labs/mw-host-agent:master",
"cpu": 100,
"memory": 512,
"portMappings": [
{
"name": "mw-agent-9319-tcp",
"containerPort": 9319,
"hostPort": 9319,
"protocol": "tcp",
"appProtocol": "grpc"
},
{
"name": "mw-agent-8006-tcp",
"containerPort": 8006,
"hostPort": 8006,
"protocol": "tcp"
},
{
"name": "mw-agent-9320-tcp",
"containerPort": 9320,
"hostPort": 9320,
"protocol": "tcp"
}
],
"essential": true,
"environment": [
{
"name": "MW_API_KEY",
"value": "<Your MW API Key here>"
},
{
"name": "MW_TARGET",
"value": "<Your MW Target here>"
}
],
"mountPoints": [
{
"sourceVolume": "docker-sock",
"containerPath": "/var/run/docker.sock",
"readOnly": false
},
{
"sourceVolume": "proc",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/proc",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "dev",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/dev",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al2_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/sys/fs/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al1_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al2_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/sys/fs/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al1_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "docker-containers-root",
"containerPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "var-log-host",
"containerPath": "/var/log",
"readOnly": true
}
],
"volumesFrom": [],
"privileged": true,
"systemControls": []
}
],
"networkMode": "bridge",
"volumes": [
{
"name": "docker-sock",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/var/run/docker.sock"
}
},
{
"name": "proc",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/proc"
}
},
{
"name": "dev",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/dev"
}
},
{
"name": "al1_cgroup",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/cgroup"
}
},
{
"name": "al2_cgroup",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/sys/fs/cgroup"
}
},
{
"name": "docker-containers-root",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/var/lib/docker/containers"
}
},
{
"name": "var-log-host",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/var/log"
}
}
],
"requiresCompatibilities": [
"EC2"
],
"pidMode": "host"
}AWS VPC Network Mode
{
"family": "mw-agent-task",
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "mw-agent",
"image": "ghcr.io/middleware-labs/mw-host-agent:master",
"cpu": 100,
"memory": 512,
"portMappings": [
{
"name": "mw-agent-9319-tcp",
"containerPort": 9319,
"hostPort": 9319,
"protocol": "tcp",
"appProtocol": "grpc"
},
{
"name": "mw-agent-8006-tcp",
"containerPort": 8006,
"hostPort": 8006,
"protocol": "tcp"
},
{
"name": "mw-agent-9320-tcp",
"containerPort": 9320,
"hostPort": 9320,
"protocol": "tcp"
}
],
"essential": true,
"environment": [
{
"name": "MW_API_KEY",
"value": "<Your MW API Key here>"
},
{
"name": "MW_TARGET",
"value": "<Your MW Target here>"
}
],
"mountPoints": [
{
"sourceVolume": "docker-sock",
"containerPath": "/var/run/docker.sock",
"readOnly": false
},
{
"sourceVolume": "proc",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/proc",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "dev",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/dev",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al2_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/sys/fs/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al1_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al2_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/sys/fs/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "al1_cgroup",
"containerPath": "/rootfs/cgroup",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "docker-containers-root",
"containerPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers",
"readOnly": true
},
{
"sourceVolume": "var-log-host",
"containerPath": "/var/log",
"readOnly": true
}
],
"volumesFrom": [],
"privileged": true,
"systemControls": []
}
],
"networkMode": "awsvpc",
"volumes": [
{
"name": "docker-sock",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/var/run/docker.sock"
}
},
{
"name": "proc",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/proc"
}
},
{
"name": "dev",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/dev"
}
},
{
"name": "al1_cgroup",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/cgroup"
}
},
{
"name": "al2_cgroup",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/sys/fs/cgroup"
}
},
{
"name": "docker-containers-root",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/var/lib/docker/containers"
}
},
{
"name": "var-log-host",
"host": {
"sourcePath": "/var/log"
}
}
],
"requiresCompatibilities": [
"EC2"
],
"pidMode": "host"
}Step 2: Register Your Task Definition File
You can register your Task Definition File using the the AWS CLI or the Amazon Web Console.
Execute the following command to register your Task Definition File in AWS. Learn more about the Amazon ECS CLI here.
aws ecs register-task-definition --cli-input-json file://<mw-ecs-agent.json>Complete the following steps in the AWS Management Console to register your Task Definition File.
- Log in to your AWS Management Console and navigate to the Elastic Container Service (ECS) section
- In the left-hand menu, click on Task Definitions
- Create a new Task Definition under the JSON tab
- Copy and paste the configuration from your Task Definition file
- Save your Task Definition JSON file
- Click Create to register the Task Definition in AWS
Step 3: Schedule the MW Agent as a Daemon Service
Set up the MW Agent Task Definition as a Daemon Service to ensure only one MW Agent container is running on each EC2 instance of the ECS cluster.
Select the appropriate tab depending on the network mode you opted for in Step 1: Create & Configure a MW Agent ECS Task Definition.
Log in to your AWS Management Console and navigate to the Elastic Container Service (ECS) section.
Choose the ECS cluster on which you intend to run the MW Agent.
Create a new service within the selected cluster by clicking the Create button.
Setup the Environment section:
a. Select Launch type under compute options.
b. Select EC2 as the Launch type.
Setup the Deployment Configuration section:
a. Select Service as the Application type.
b. Specify the Task Definition you had registered earlier in Step 2: Register Your Task Definition File section. Select the appropriate revision you want to run. This will most likely be the LATEST revision.
c. Provide a unique Service Name.
d. Choose DAEMON as the Service Type to ensure one MW Agent container runs on each EC2 instance.
If you are running MW Agent in Host or Bridge (Default) network mode, then skip to Step 7.
If you are running MW Agent in AWSVPC network mode, then select Service discovery to expand and check the box with label Use service discovery. Checking this box should provide more configuration options.
Your screen should look like below
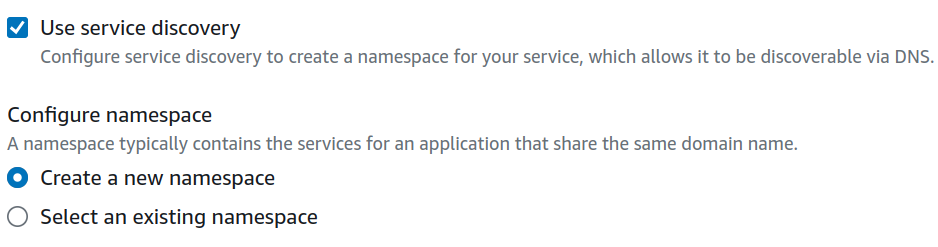
a. Under Configure namespace, you have two options. Choose one of the options below
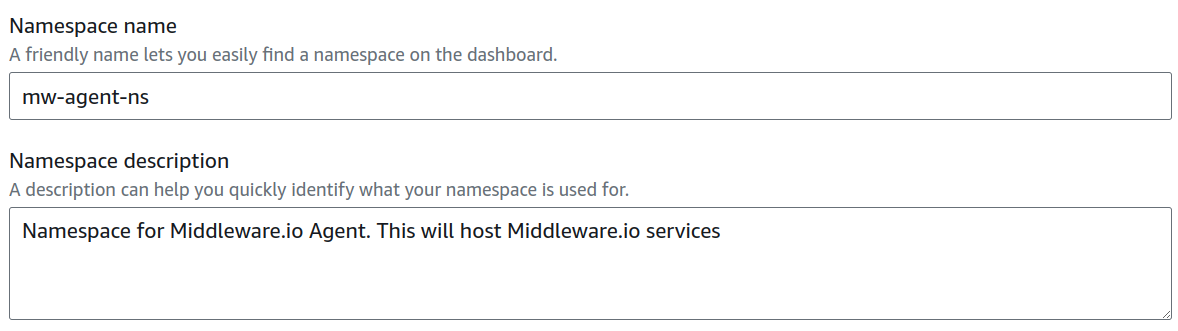
- Create a new namespace: If you do not have an existing namespace under which you want to run MW Agent service, you can create a new namespace by clicking on the Create a new namespace option and giving namespace name and description.
The AWS console should look like the picture below
- Select an existing namespace: If you already have a namespace under which you want to create a service discovery endpoint, check Select an existing namespace option and select the namespace in which you want to run MW Agent service. Usually, this will be the same namespace of the cluster on which you are creating the service.
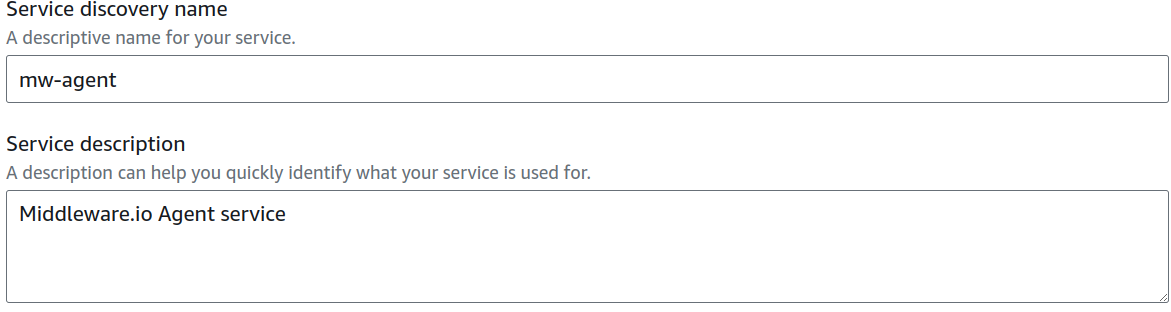
b. Under Configure service discovery service, select Create a new service discovery service.
- For Service discovery name, enter mw-agent as the service discovery name. Optionally, you can provide the service description under the Service description field.
AWS console should look like the picture below
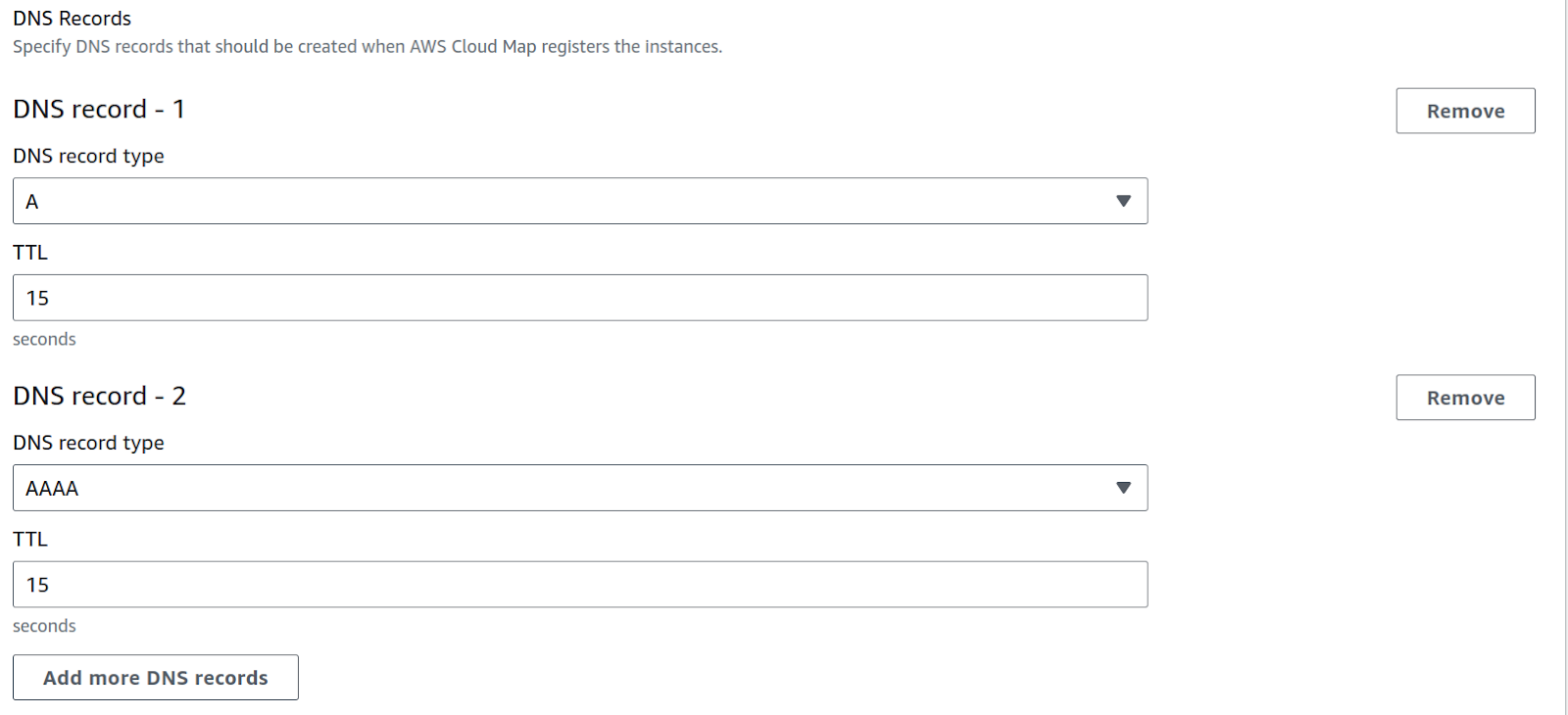
- Leave Enable Amazon ECS task health propagation checked.
- If you have IPv6 enabled in your VPC, click on the Add more DNS records button and select AAAA from the DNS record type. Keep TTL value to 15 seconds.
The AWS console should like the picture below for DNS configuration.
Proceed to create the service.
Container Trace and Log Collection
Begin collecting container trace and log data in your EC2 instance. The MW Agent will collect ECS container logs emitted to the stdout and stderr log stream and receive traces from your application and send to your Middleware account.
The MW Agent must be running as an app before setting up collection. If not, attempted trace collection will throw an error while connecting to the agent and logs will not be sent at all.
Modify your Application Task Definition
You can setup container trace and log monitoring by modifying your Task Definition JSON file or following the below steps in the AWS Management Console.
- To collect traces, configure the
MW_AGENT_SERVICEenvironment variable in your application's Task Definition. - To collect logs, configure the
logConfigurationsection to enable thefluentdlogging driver in your application's Task Definiton.
Below is the sample configuration you need to add in your application's Task Definition. Select the configuration depending on the network mode of MW Agent in the the section Step 1: Create & Configure a MW Agent ECS Task Definition
"containerDefinitions": [
{
(...)
"environment": [
{
"name": "MW_AGENT_SERVICE",
"value": "172.17.0.1"
}
],
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "fluentd",
"options": {
"fluentd-address": "172.17.0.1:8006"
}
}
(...)
}
]In the following configuration, replace <mw-agent service_discovery_name.service_discovery_namespace> with MW Agent's service discovery name and namespace configured in Step 3: Schedule the MW Agent as a Daemon Service above.
For example, if MW Agent service discovery name is mw-agent and namespace name is mw-agent-ns, replace <mw-agent service_discovery_name.service_discovery_namespace> with mw-agent.mw-agent-ns in the configuration below.
"containerDefinitions": [
{
(...)
"environment": [
{
"name": "MW_AGENT_SERVICE",
"value": "<mw-agent service_discovery_name.service_discovery_namespace>"
}
],
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "fluentd",
"options": {
"fluentd-address": "<mw-agent service_discovery_name.service_discovery_namespace>:8006"
}
}
(...)
}
]Navigate to the Amazon Elastic Container Service section in the AWS Management Console.
Click on the Task Definition and select your desired Task Definition.
Create a new revision
Skip steps 4 or 5 if you do not want to enable container traces or logs
Enable container traces in your application
a. Under the
Environment Variablessection, selectAdd environment variableb. Add
MW_AGENT_SERVICEenvironment variable and set the value to172.17.0.1if you are running MW Agent underHostorBridge (Default)network mode.If you are running MW Agent under
AWSVPCnetwork mode, set it to MW Agent's service discovery name configured in Step 3: Schedule the MW Agent as a Daemon Service. For example, if MW Agent's service discovery name ismw-agentand the namespace ismw-agent-ns, setMW_AGENT_SERVICEenvironment variable tomw-agent.mw-agent-ns.Enable container logging in your application:
a. Navigate to Logging.
b. Check
Use logging collection.c. Add Parameters as seen below
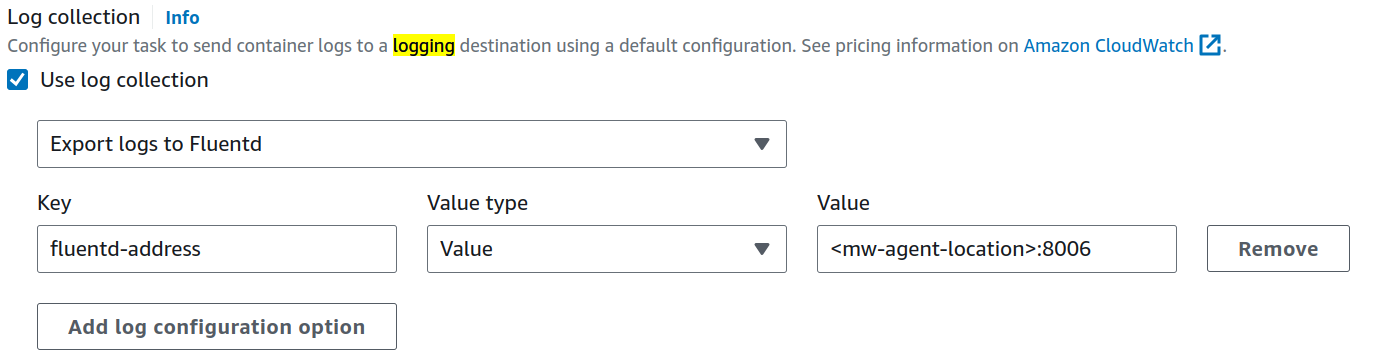
If MW Agent is running under
HostorBridge (Default)network mode, replace<mw-agent-location>with172.17.0.1. So theValuein above configuration would look like172.17.0.1:8006.If MW Agent is running under
AWSVPCnetwork mode, replace<mw-agent-location>with MW Agent's service discovery name configured in Step 3: Schedule the MW Agent as a Daemon Service. For example, if MW Agent's service discovery name ismw-agentand the namespace ismw-agent-ns, theValuein the above configuration will bemw-agent.mw-agent-ns:8006.Click Create to update your Task Definition
Update the Services/Daemon definition to use the latest version of your application's Task Definition
ADOT Collector Setup
Use the ADOT Collector for AWS ECS integration in AWS EC2 or AWS Fargate to monitor your applications without having to manage servers. This involves creating or updating a task definition to have the following two container definitions:
- Primary Application Container: Hosts the main application that emits telemetry.
- ADOT Collector Container: Collects, processes, and exports telemetry data.
Create the ADOT Collector Container
For Each ECS Task that you want to monitor, add the following sidecar container to your containerDefinitions array.
You need to carefully set MW_API_KEY and MW_TARGET values while setting the environment variable - OTEL_CONFIG_CONTENT.
The environment variable OTEL_CONFIG_CONTENT needs to preserve the exact same formatting as given below. If not, the metrics might not be exported properly.
{
"name": "adot-collector",
"image": "public.ecr.aws/aws-observability/aws-otel-collector:latest",
"cpu": 256,
"portMappings": [],
"essential": true,
"command": [
"--config=env:OTEL_CONFIG_CONTENT"
],
"environment": [
{
"name": "OTEL_CONFIG_CONTENT",
"value": "receivers:\n awsecscontainermetrics:\n collection_interval: 20s\nprocessors:\n batch:\n send_batch_size: 1000\n send_batch_max_size: 1000\n timeout: 30s\nexporters:\n prometheus:\n endpoint: \"0.0.0.0:9999\"\n otlphttp/2:\n endpoint: \"<Your MW_TARGET here>\"\n headers:\n Authorization: \"<Your MW_API_KEY here>\"\n sending_queue:\n enabled: false\n num_consumers: 100\n queue_size: 10000\n tls:\n insecure: true\n insecure_skip_verify: true\n# insecure: false\n debug:\n verbosity: detailed\n\nservice:\n pipelines:\n metrics:\n receivers: [awsecscontainermetrics]\n processors: [batch]\n exporters: [otlphttp/2]\n\n"
}
],
"mountPoints": [],
"volumesFrom": [],
"logConfiguration": {
<Setup Log Configurations as per your requirement>
}
}Collect Metrics
Adding the ADOT Collector sidecar container mentioned above will automatically collect metrics data from your ECS tasks and containers.
Visualize Your Data
Quickly access your Amazon ECS data with Middleware’s default ECS dashboard. Navigate to the Dashboard Builder and select the ECS Metrics Dashboard.
Your AWS ECS data comes from the awsecscontainermetricsreceiver whereas your container data comes from the dockerstatsreceiver.
Troubleshooting
Missing Integrations Menu
If you do not see the Integrations Menu in Middlware, that means your account has not been granted Installation permissions. Contact your system administrator to add the Installation permission to your user role in Settings.
Need assistance or want to learn more about Middleware? Contact our support team at [email protected] or join our Slack channel.