PostgreSQL Integration
The PostgreSQL integration enables you to ingest performance and health metrics from your PostgreSQL instance(s) into Middleware, allowing you to track blocks read versus hits, table/index sizes, transactions (including commits/rollbacks), per-statement activity, and more.
Prerequisites
- Middleware Host Agent is installed on the host that can reach your PostgreSQL instance. See Installing the Agent
Setup
1 Enable pg_stat_statements
pg_stat_statements exposes per-statement stats that the integration relies on.
- Edit postgresql.conf. (path example below; adjust for your distro/version)This ensures the extension is preloaded and IO timing is captured for accurate statement metrics. Save the file.
# /etc/postgresql/14/main/postgresql.conf shared_preload_libraries = 'pg_stat_statements' pg_stat_statements.track = all pg_stat_statements.max = 10000 track_io_timing = on - (Alternative via SQL): As a superuser, you can also set the preload parameter from SQL (still requires a restart to take effect):
ALTER SYSTEM SET shared_preload_libraries = 'pg_stat_statements'; - Restart PostgreSQL for the preload to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart postgresql - Verify the extension and data flow (as superuser):
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pg_stat_statements; SELECT calls, query FROM pg_stat_statements LIMIT 1;
You should see a row like:
calls | query
------+-------------------------------
8 | SELECT * FROM t WHERE field = ?(Your values will differ. This view reflects your executed statements.)
2 (optional): Create a least-privileged user
If you don’t want to use the superuser for monitoring, create a read-only user with just what’s needed:
- Create the userVerify:
CREATE USER lpu WITH PASSWORD 'pass';You should see lpu in the roles listing.\du - Grant minimal access
-- allow connections to the database you'll monitor GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE <your_db_name> TO lpu; -- permit reading statement stats GRANT SELECT ON pg_stat_statements TO lpu; -- permit reading global stats where needed GRANT pg_read_all_stats TO lpu;
Test with the lpu account:
SELECT calls, query FROM pg_stat_statements LIMIT 1;(The output will reflect queries observed under your workload.)
3 Create a Credentials File
On the host where the Middleware Host Agent runs, create a small YAML file with connection details:
# /home/ubuntu/postgres_creds.yaml
postgresql:
endpoint: localhost:5423
username: postgres # or the user you created in Step 2
password: postgres # or that user's passwordUse the actual host/port for your deployment (the example uses localhost:5423). The file path you choose will be referenced inside Middleware in Step 5.
4 Open the Integration in Middleware
In Middleware, go to Installations → All Integrations → PostgreSQL. This is where you’ll bind a host and point Middleware to your credentials file.
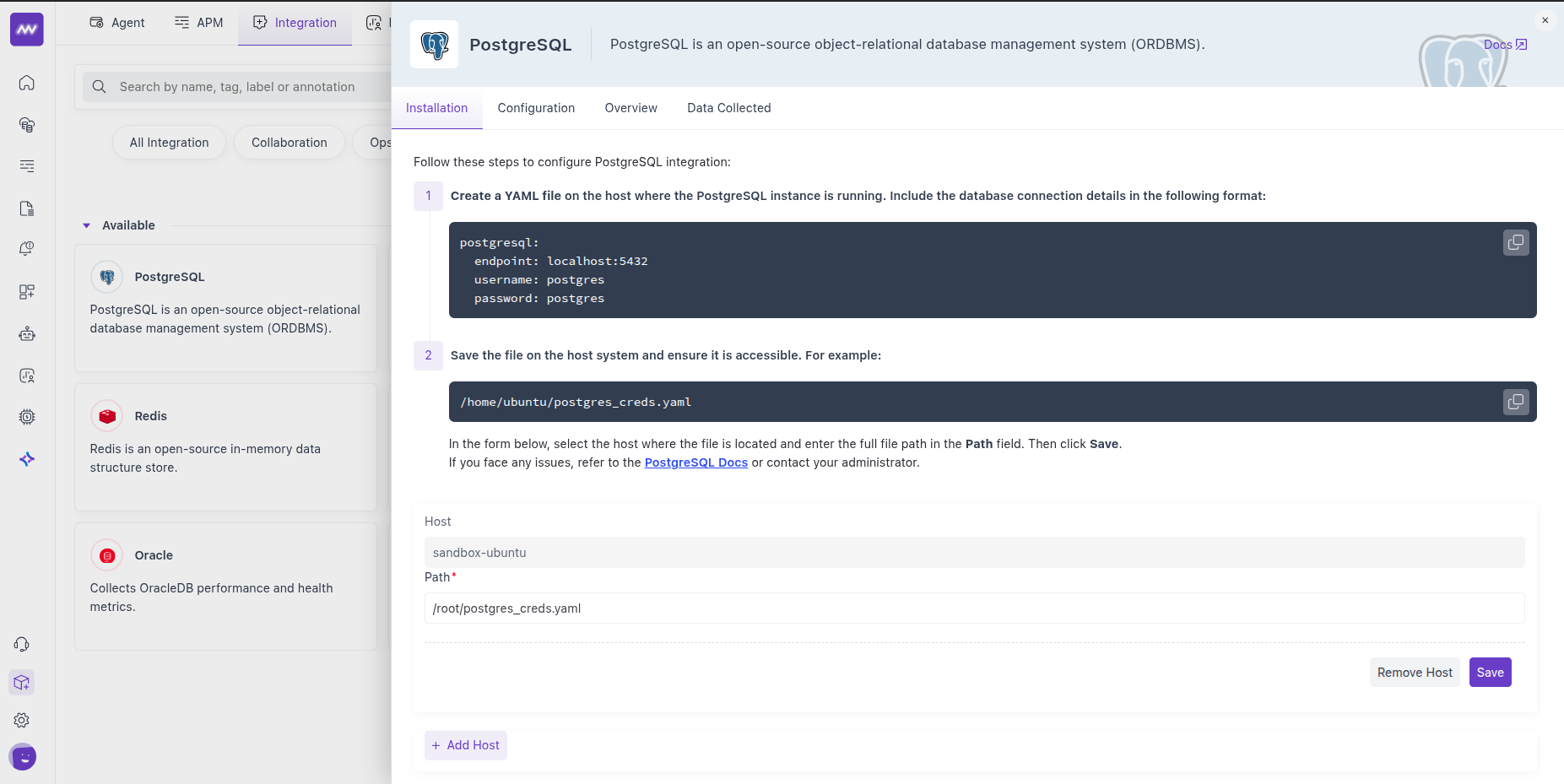
5 Enable the Integration
In the PostgreSQL integration form:
- Select the host (from the dropdown) where the cred file resides.
- Enter the credentials file path (from Step 3).
- Click Save.
Once saved, the integration starts ingesting metrics.
Visualise your Data
Default PostgreSQL Dashboard
After setup, Middleware adds a PostgreSQL dashboard to the Dashboard Builder. Use it as a starting point to explore key DB metrics without building widgets from scratch.
Create Custom Widgets
When adding a widget, choose data source postgresql to browse all exposed metrics and craft charts for your SLOs or run-book checks.
Alerts
You can alert on any PostgreSQL metric. Create a rule using Database as the detection method and PostgreSQL as the database type; the Metrics dropdown then lists all available metrics for this integration. Configure conditions, thresholds and recipients as usual.
Metrics Collected
Core Engine & Storage
| Metric Name | Description |
|---|---|
postgresql.backends | Number of backends |
postgresql.blocks_read | Number of disk blocks read |
postgresql.buffer_hit | Disk block hits in buffer cache (avoids reads), tagged with database name |
postgresql.db_size | Database disk size |
postgresql.database.count | Count of databases in a cluster |
postgresql.index.scans | Number of index scans on a table |
postgresql.index.size | Size of the index on disk |
postgresql.table.count | umber of user tables in a database |
postgresql.table.size | Disk space used by a table |
postgresql.table.vacuum.count | Number of times a table has been manually vacuumed |
Transactions & Row Activity
| Metric Name | Description |
|---|---|
postgresql.commits | Number of transactions committed |
postgresql.rollbacks | Number of rollbacks |
postgresql.rows | Number of rows in the database |
postgresql.rows_inserted | Rows inserted |
postgresql.rows_updated | Rows updated |
postgresql.rows_deleted | Rows deleted |
postgresql.rows_fetched | Rows fetched |
postgresql.operations | Number of DB row operations |
Checkpointing & Background Writer
| Metric Name | Description |
|---|---|
postgresql.bgwriter.checkpoint.count | Checkpoints performed |
postgresql.bgwriter.duration | Total time spent in checkpoint processing (ms) |
postgresql.bgwriter.maxwritten | Times bgwriter stopped a cleaning scan after writing too many buffers |
postgresql.bgwriter.buffers.writes | Buffers written |
postgresql.bgwriter.buffers.allocated | Buffers allocated |
Connections & Limits
| Metric Name | Description |
|---|---|
postgresql.connection.max | Configured max number of client connections allowed |
Statement-level (via pg_stat_statements)
| Metric Name | Description |
|---|---|
postgresql.query.count | Number of times the (normalised) statement was executed |
postgresql.query.total_exec_time | Total wait time of the normalised timed events (ns) |
Live Row Estimates
| Metric Name | Description |
|---|---|
postgresql.live_rows | Approximate number of live rows (tagged with relation name) |
Troubleshooting
“Integrations” menu not visible
If you don’t see Integrations in Middleware, your account probably lacks Installation permissions. Ask an admin to add Installation to your role in Settings.
Need assistance or want to learn more about Middleware? Contact our support team at [email protected] or join our Slack channel.