Error Tracking
Use Error Tracking to detect, group, and debug front‑end errors captured by Middleware’s RUM SDK. This page documents the Errors list and the Error details view , plus best practices for source maps, release hygiene, and privacy.
Purpose
- Surface stability issues across browsers, regions, and app versions.
- Unminify and inspect stack traces with source maps to move from a symptom to the exact line of code.
- Jump into session replay for user‑level context and reproduce conditions quickly.
Access & Scope
Real User Monitoring → Applications → Error tracking

The time range selector (top‑right) controls the data shown. Auto‑refresh is on by default; click Pause while investigating.
Errors List (Dashboard)
The Errors page opens with a high‑level trend and a grouped table.
Errors Trend
A time series of total error instances across the selected range. Use it to spot spikes and confirm when a regression started.
Table Columns
Each row aggregates an error group (same message + stack signature):
- Name – normalized error title (e.g., Loading chunk 3527 failed…).
- Error Type – category such as
error(code),xhr(network), orconsoleError. - Instances – count of occurrences in range.
- Last Occurrence / First Occurrence – recency & onset for the group.
- Affected Users – distinct users (sessions) hit by the error.
Search at the top, sort any column, and click a row to open Error details. The Share button copies a deep link to collaborate.
Error Details
The details view explains a single error group with stack traces, summary tiles, properties, and links to Relevant Sessions.
Summary Tiles
- Affected Users – distinct users touched by this error group in the time window.
- Instances – occurrences of this error group.
- Last/First Occurrence – helps correlate with deployments.
- Errors over time – per‑group time‑series for onset analysis.
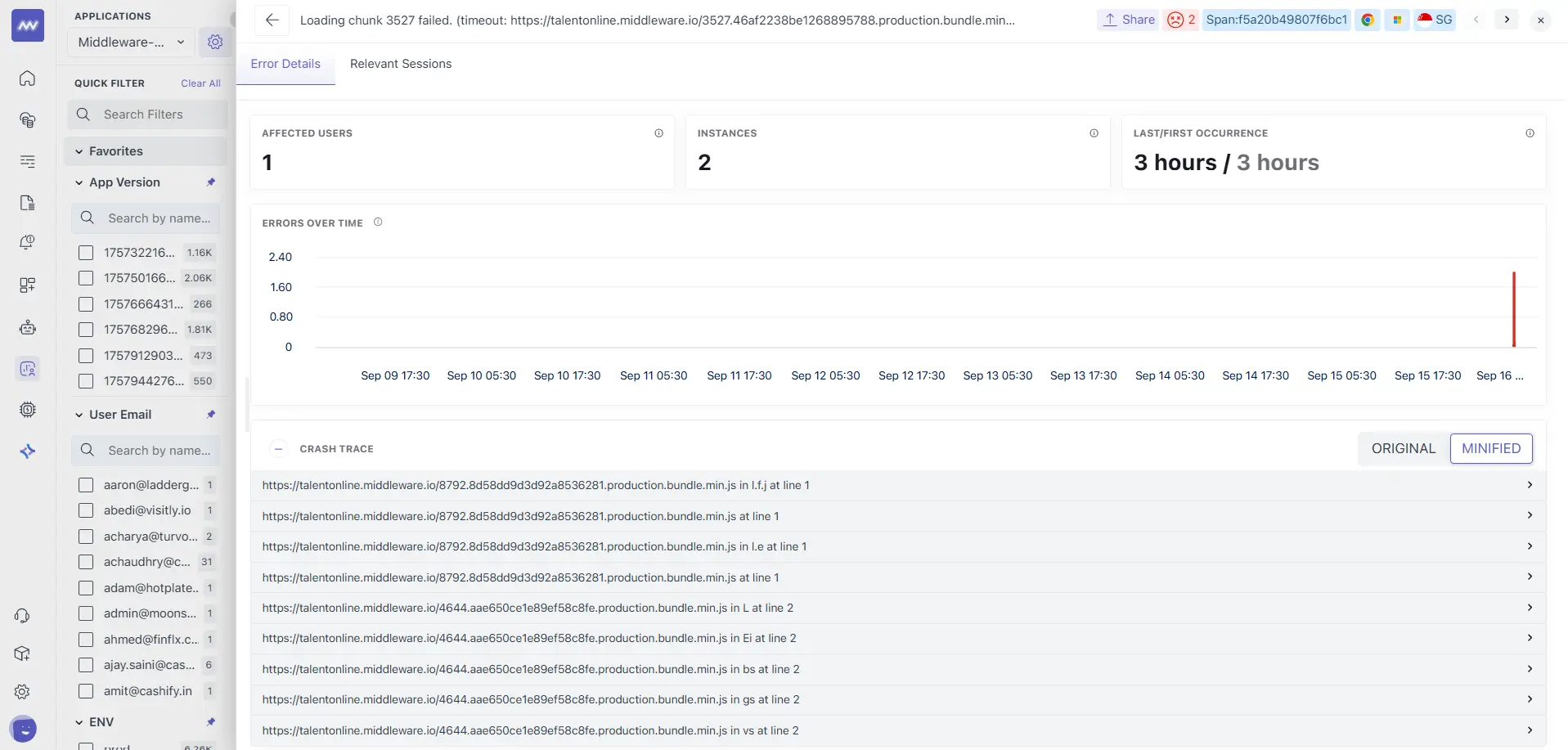
Crash Trace
An expandable stack section with an ORIGINAL / MINIFIED toggle:
- MINIFIED shows the stack as the browser recorded it (useful when source maps are missing).
- ORIGINAL uses uploaded source maps to unminify and annotate frames with original filenames, line and column numbers.
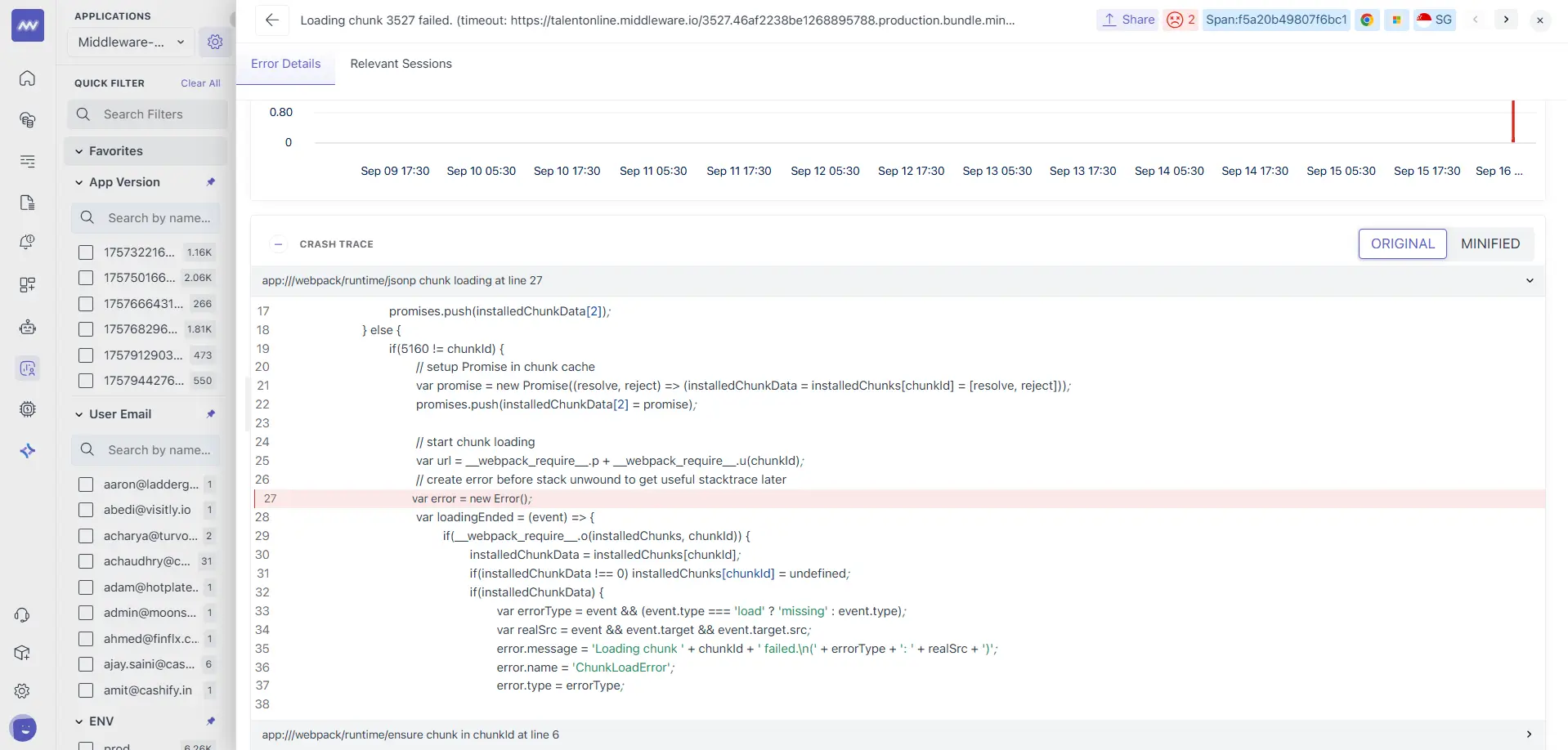
- For multi‑bundle apps (e.g., webpack code‑splitting), frames include runtime and chunk loaders. Use the first app frame as your starting point.
If you see only minified frames, upload source maps for the corresponding build and ensure the release version matches your app.version. See Source maps below.
Properties
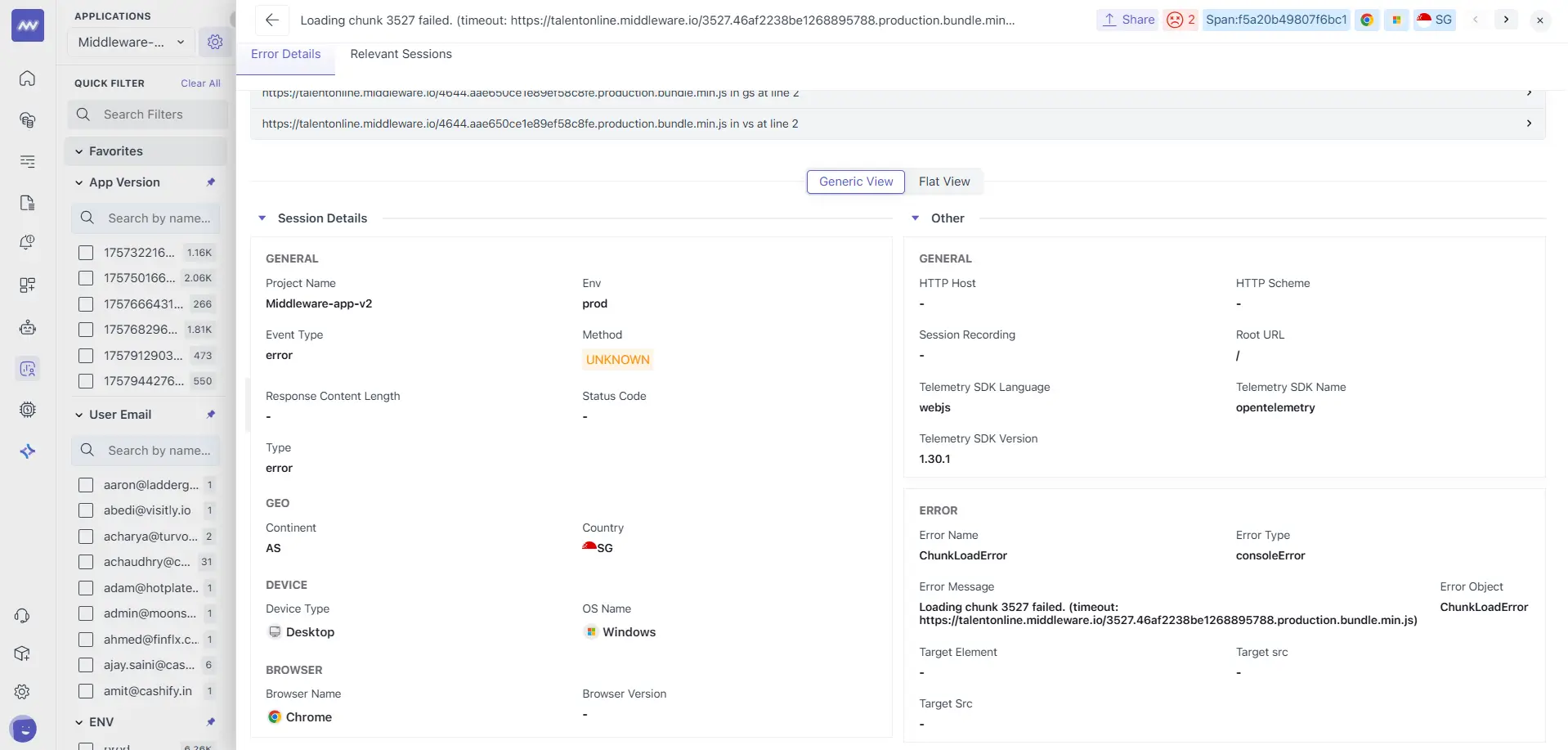
Switch between Generic View and Flat View to inspect all collected attributes for an instance. Common fields include:
- Error attributes:
error.name,error.message,error.stack,error.type(e.g.,consoleError),level(severity). - Event / View context:
event.type(error),view_count,action_count,frustration_count,page.href,root.url. - Session & user:
session.id, identified user attributes (if set). - Browser & device:
browser.name/browser.version,os.type/os.version,device.type. - Telemetry:
telemetry.sdk.name(e.g.,opentelemetry),telemetry.sdk.language(webjs),sdk.version.
Relevant Sessions
A tab that lists sessions where this error occurred. Open a session to launch the Session Player directly at the timestamp; use Network and Events to correlate failing requests, long tasks, and user actions.
Workflows
Triage a spike from the Errors list
- Set Time range to when the spike started; click the spike on Errors Trend.
- Add App Version and ENV filters; open the top row by Instances or Affected Users.
- In Error details, scan Errors over time and Crash trace (switch to ORIGINAL).
- Open Relevant Sessions → replay and check Network/Events around the timestamp.
- Create an alert or issue; share the error link for collaboration.
Debug a ChunkLoadError (dynamic import failure)
- In Crash trace, find the first app frame near
jsonp chunk loading/ runtime loader. - In Relevant Sessions, open a session → Network: confirm the chunk request timed out/failed or was blocked (status 0).
- Fixes to consider: improve caching/TTL on your CDN, prefetch/preload critical chunks, handle
import()errors gracefully with retry, ensure build IDs and cache busting are consistent. - After rollout, filter by the new App Version and ensure Instances drop to zero.
Investigate Network/XHR Errors
- Filter Error Type = xhr.
- Open the group; in Properties, review request URL/context, then jump to a Relevant Session and use the Network tab.
- Check CORS, authentication, and backend error responses; correlate with APM traces if tracing is enabled.
Best Practices
- Set
app.versionandenvat SDK init for clean comparisons and source‑map matching. - Capture user identity (optional) to unlock Affected Users diagnostics and user‑level filtering.
- Use alerts to watch for regressions in error rate or specific groups; include
browser.trace = truein alert filters to attach RUM context. - Mask sensitive data in session recordings and logs to avoid storing PII in errors or replays.
Troubleshooting
- Only MINIFIED stacks → source maps not uploaded, or
appVersion≠app.versionfor that release; upload maps for the current build. - Status = 0 in sessions’ Network tab → request blocked or network dropped; check CSP, ad‑blockers, or CORS.
- Instances high but Affected Users low → many repeats from a single page (e.g., polling failure). De‑duplicate in code and rate‑limit error logging.
- No data after deploy → confirm RUM script loads early and your new build sets
app.version.
Privacy & Governance
- Middleware masks sensitive inputs by default; use CSS classes and recording options to expand or restrict masking as needed.
- Share error links only with authorized teammates; original stacks can expose file paths and identifiers.
Need assistance or want to learn more about Middleware? Contact our support team at [email protected] or join our Slack channel.