Middleware Pipelines Overview
Middleware Pipelines define how telemetry moves from source to storage, and how that data is collected, filtered, modified, and stored along the way. This gives teams control over logs, metrics, traces, and RUM before data is persisted.
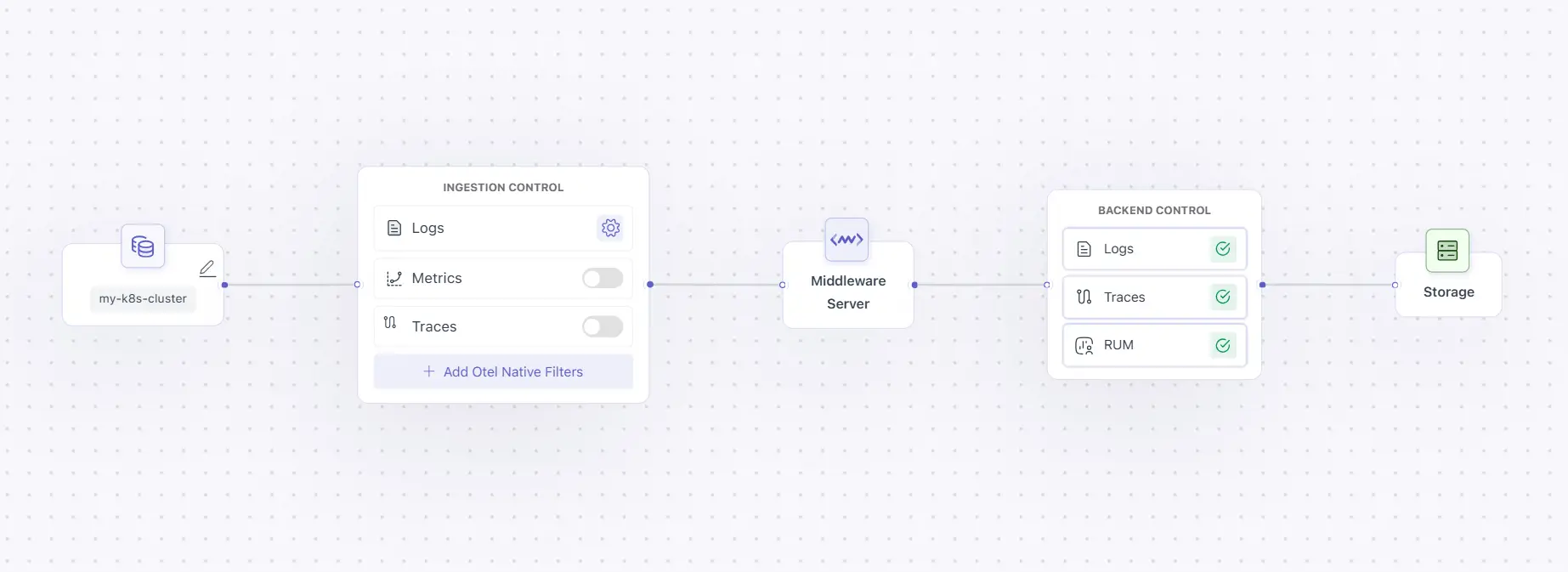
A pipeline follows this path:
Source → Ingestion Control → Server→ Backend Control → Storage
What is a Pipeline?
A pipeline in Middleware is the data path that controls telemetry lifecycle from intake to storage. It is built so teams can manage data quality and relevance before storage happens.
With pipelines, you can:
- Reduce noise
- Control data volume
- Remove sensitive fields
- Apply smart filtering and transformations
Why Pipelines Exist
Without pipelines, all data from all sources is sent and stored blindly. Pipelines add control points so you can decide what is useful and what should be dropped or transformed.
With pipelines, you can:
- Drop unwanted data before it reaches storage
- Apply different rules for different hosts, clusters, or integrations
- Apply backend rules without redeploying agents
- Apply OTEL-native filters directly on agents for clusters
- Control cost, performance, and compliance
Pipeline Source Types
Every pipeline starts by selecting a source. Middleware supports three source types:
| Source Type | What it represents |
|---|---|
| Host | A single server or machine running the Middleware Agent |
| Cluster | A Kubernetes cluster running the Middleware Agent |
| Serverless | Serverless applications including managed databases, cloud services, etc. |
Each source type supports different control depth based on where data is collected and where filtering can be applied.
Pipeline Control Layers
Middleware provides three control layers inside pipelines:
| Layer | Where it runs | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Ingestion Control | Middleware ingestion layer | Modify, route, enrich, or sample data before it enters the platform |
| OTEL-Native Filters | Agent / cluster side | Drop or filter data at source before it is sent |
| Backend Control | Middleware backend | Drop data before storage based on rules |
Not every source supports all three layers. Availability depends on how data is collected for that source type.
For creating pipeline, user needs to add one or more than one processor. User can also add same processor multiple times.