Service Maps
Service Maps provide a visual, dependency-driven view of your distributed system, showing how services communicate with each other across protocols like HTTP, gRPC, and databases. Instead of navigating services in isolation, Service Maps help you understand service relationships, traffic flow, latency, and errors at a glance.
Service Maps are powered by distributed traces, allowing Middleware to automatically discover service interactions and present them as an interactive topology.
What You Can Do with Service Maps
With Service Maps, you can:
- Visualize upstream and downstream dependencies between services
- Identify high-latency or error-prone services quickly
- Drill down into service-level performance metrics
- Inspect edge-level communication details between two services
- Navigate directly to related traces and logs for faster debugging
Accessing Service Maps
Navigate to:
APM → Services → Map View
By default, services are shown in Table View. Switch to Map View to see the service dependency graph.
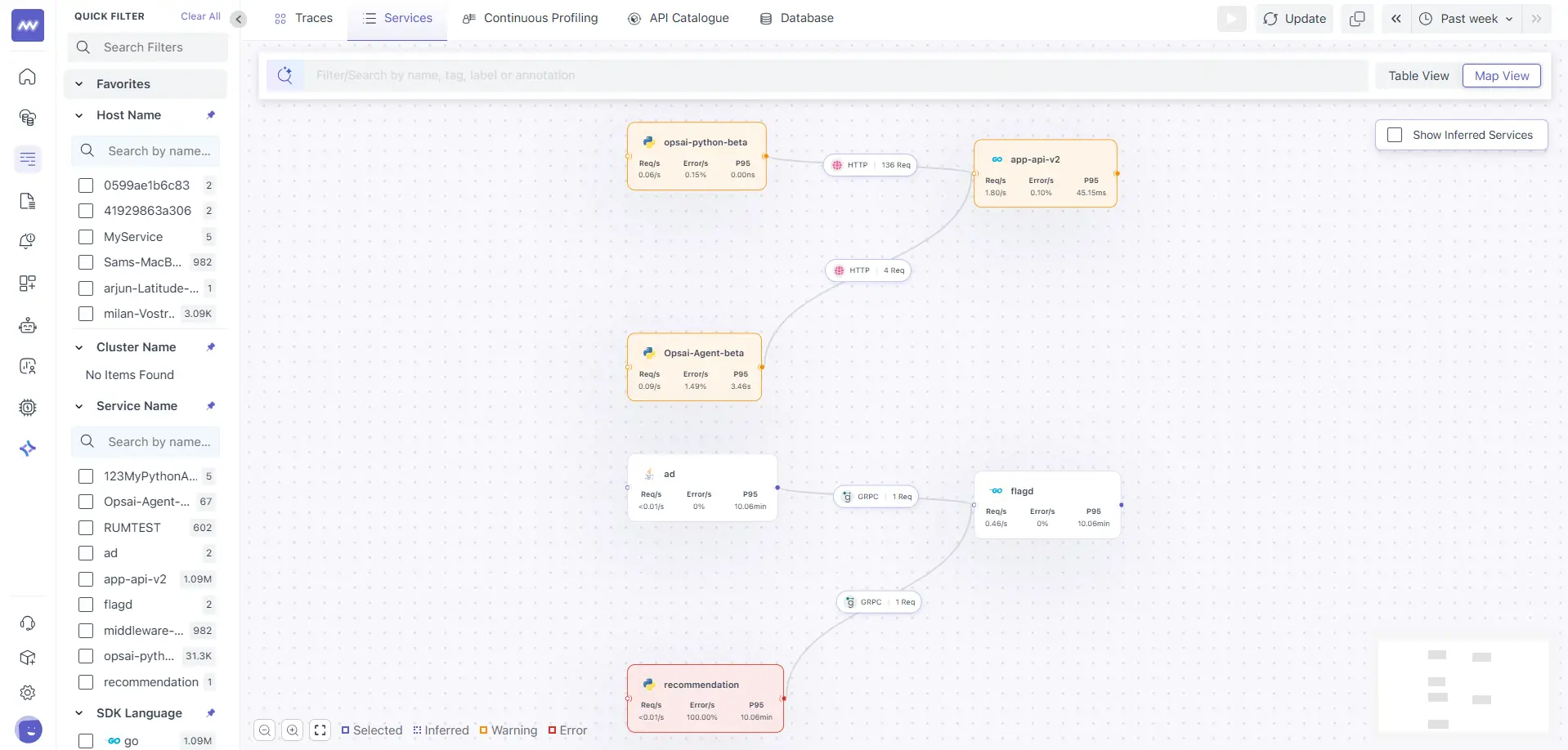
Each node in the map represents a Service Card, and the connecting lines represent Edges (service-to-service communication).
Service Cards
Service Cards are the primary building blocks of the Service Map. Each card represents an individual service detected by the Middleware.
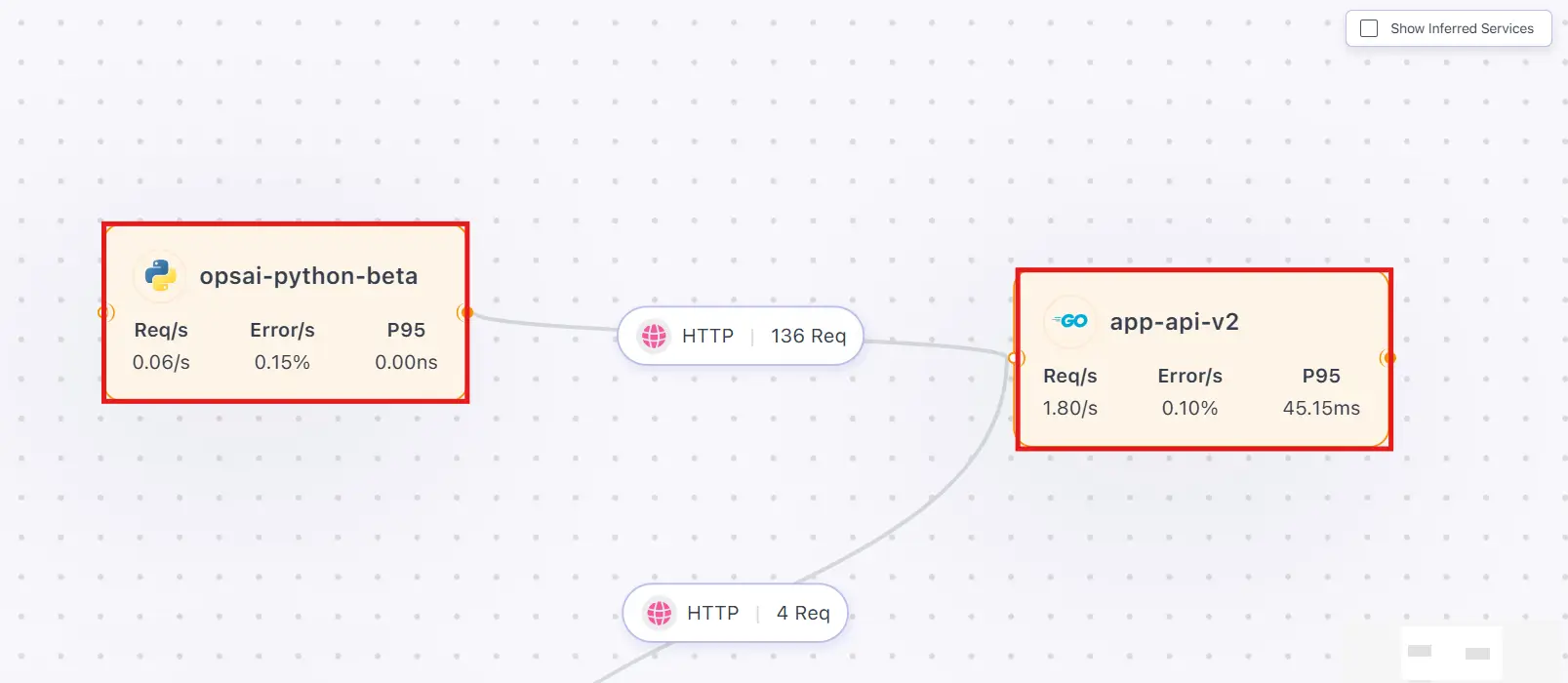
Information Displayed on a Service Card
Each service card shows:
- Service name
- Request rate (Req/s)
- Error rate
- P95 latency
- Health state, visually indicated by color:
- 🟡 Warning (Less than 5% error rate)
- 🔴 Error (More than 5% error rate)
This allows you to quickly spot problematic services without opening detailed views.
Drilling Down into a Service Card
Clicking on a service card opens a service-level drill-down view.
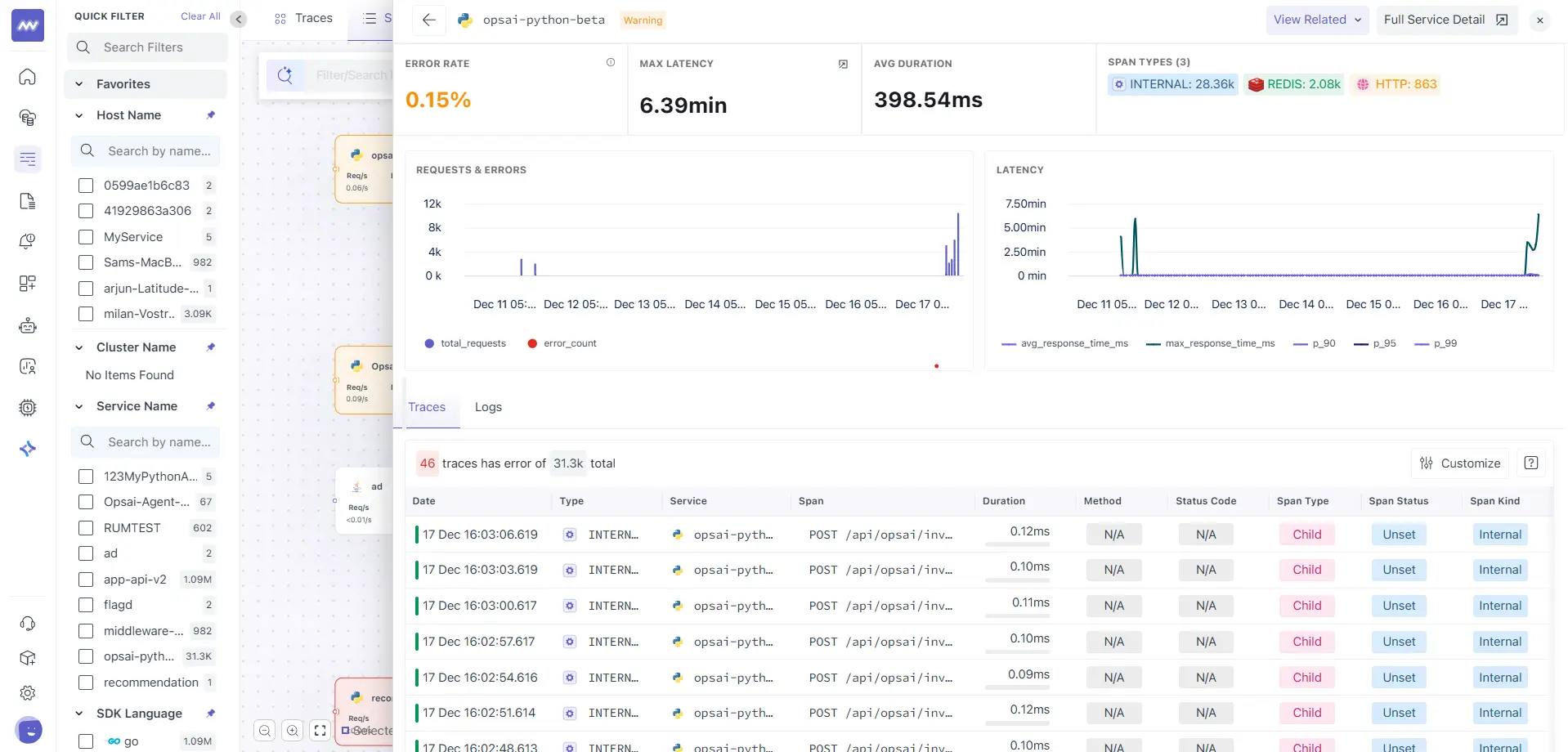
Service Drill-Down View Includes
- Error rate
- Maximum latency
- Average duration
- Request and error trends over time
- Latency percentiles (P90, P95, P99)
- Span type distribution (HTTP, Internal, Redis, Database, etc.)
This view helps you assess the health of a service over time, not just at a single moment.
Within the service drill-down, you’ll find the View Related option.
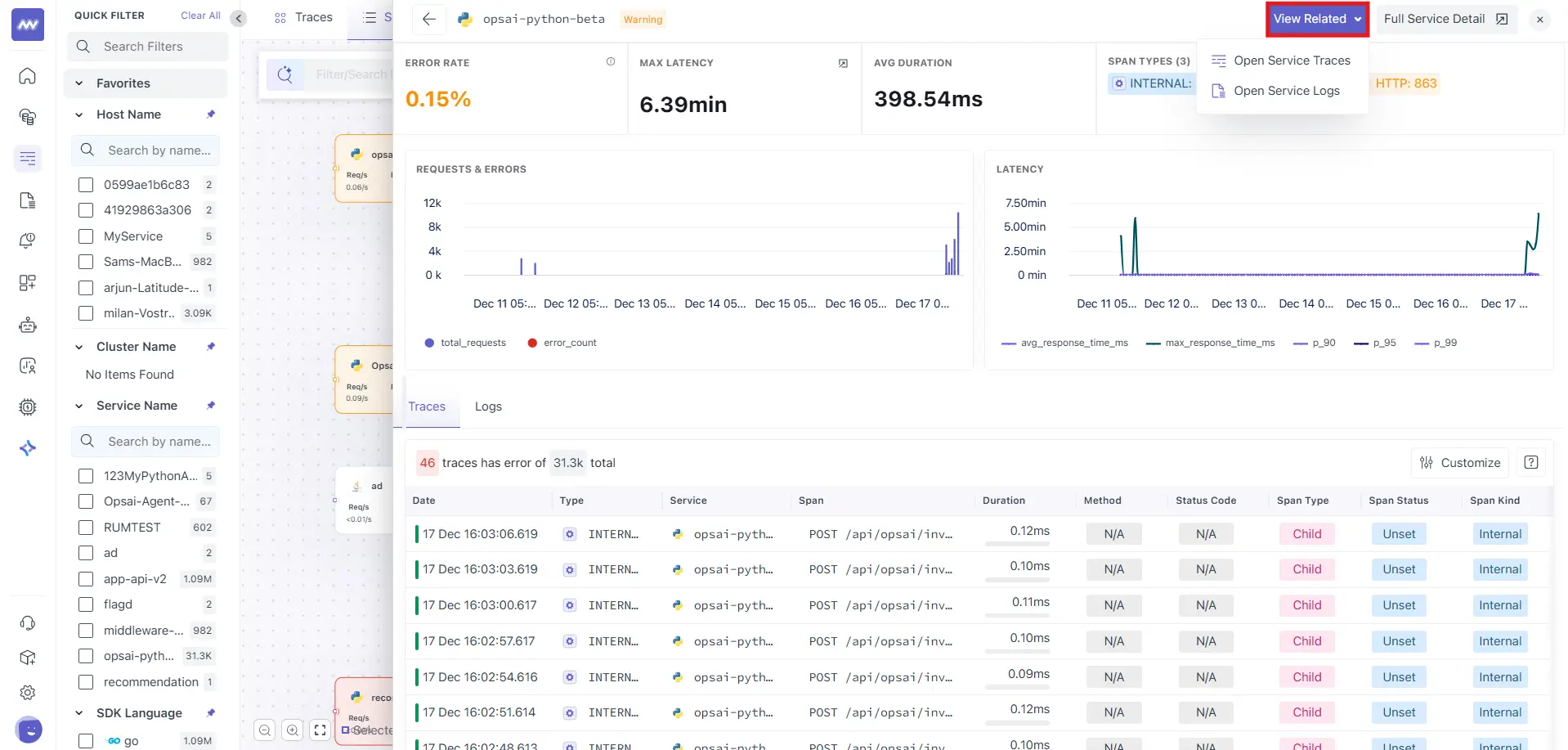
Available Actions
- Open Service Traces: Redirects you to the Traces view filtered for the selected service.
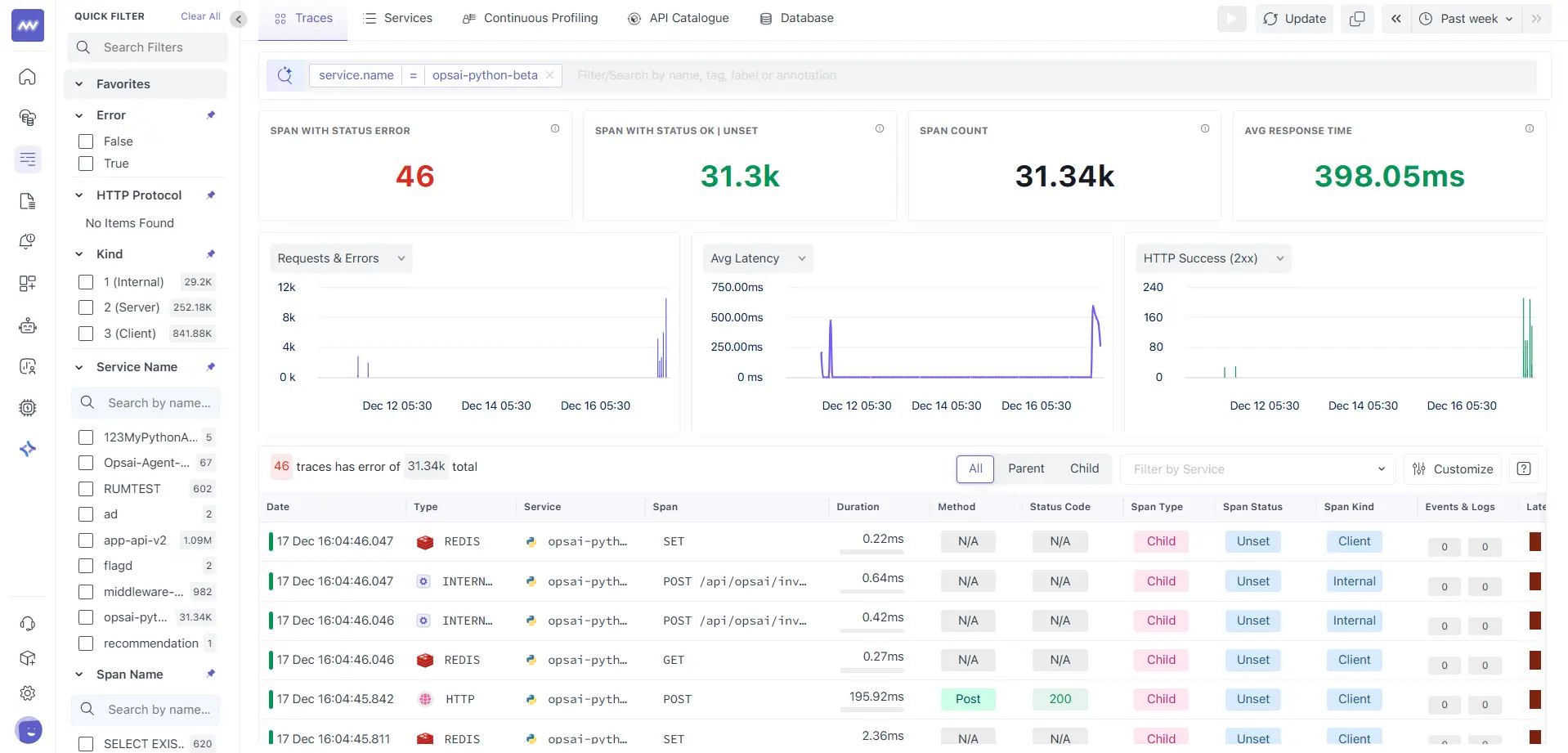
- Open Service Logs: Redirects you to Logs with the service context pre-applied.
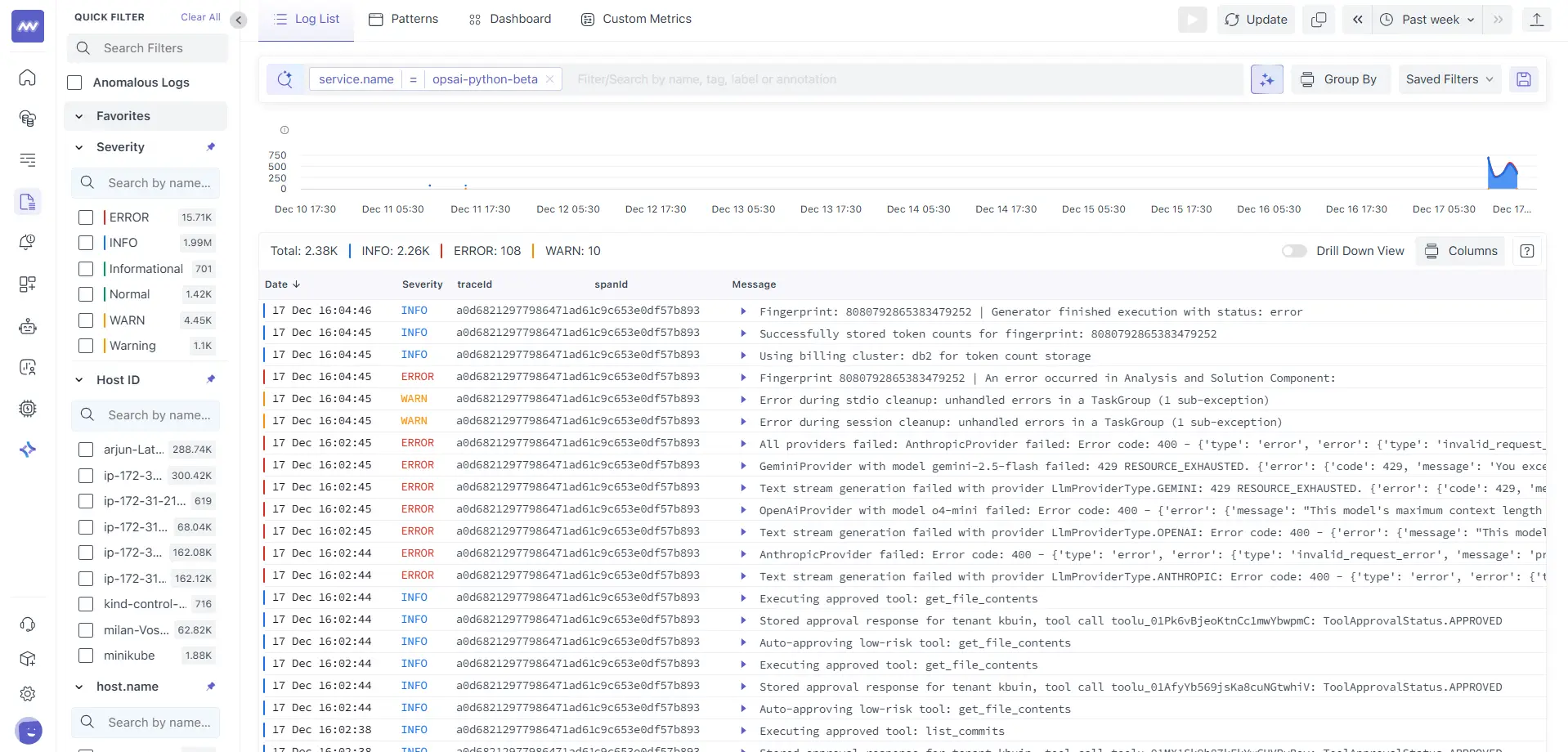
This enables one-click navigation from topology → metrics → traces → logs.
Isolated View
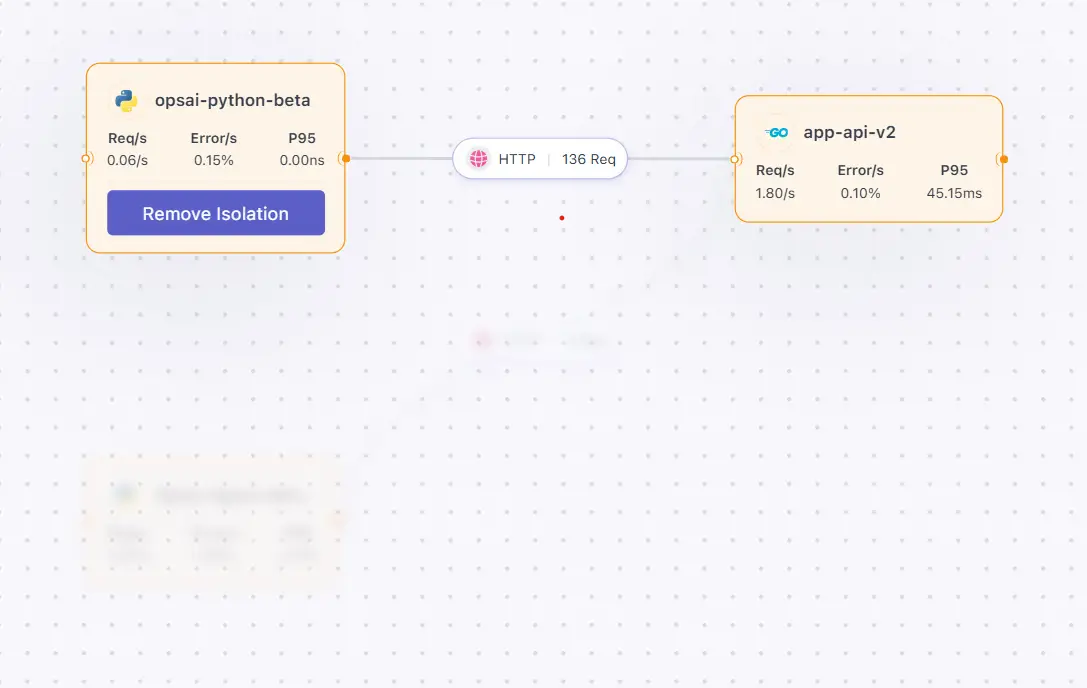
Isolated View helps you focus on a single service and its direct dependencies by visually dimming everything else in the Service Map. This makes it easier to analyze service behavior without distractions from unrelated components.
What Is an Isolated View?

When Isolated View is enabled:
- The selected service card remains fully visible
- Directly connected services (upstream and downstream) stay in focus
- All other services and edges are blurred out
- The active service is clearly highlighted for investigation
This is especially useful in large or dense service maps, where multiple services and connections can make analysis harder.
How to enable isolated view:
- Open APM → Services → Map View
- Hover over a service card
- Select Isolate View on the service card
Once enabled, the map automatically switches to an isolated context for that service.
Removing Isolation
While in Isolated View, the selected service card shows a Remove Isolation button.
Click Remove Isolation to return to the full Service Map view with all services visible again.
Service Edges (Service-to-Service Communication)
Edges represent actual communication paths between two services, inferred from traces.
Each edge shows:
- Protocol used (HTTP, gRPC, Database, etc.)
- Total request count for that interaction
Drilling Down into an Edge
Clicking on an edge opens a connection-level drill-down view.
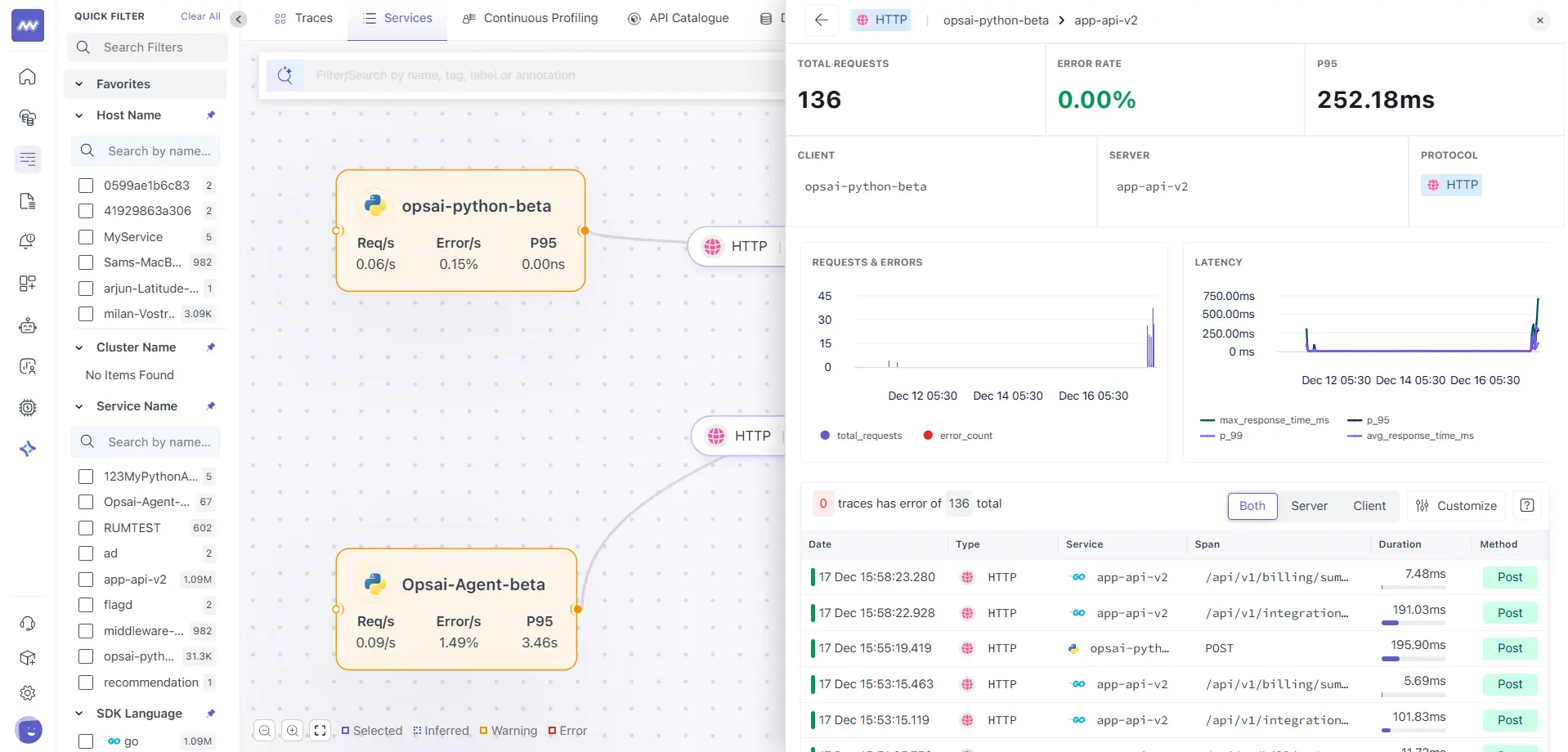
Edge Drill-Down View Includes
- Total requests
- Error rate
- P95 latency
- Client service
- Server service
- Protocol used
- Request and latency trends
- List of traces for that specific interaction
This is especially useful when:
- A service is healthy overall, but slow when calling a specific downstream service
- You want to isolate problematic dependencies
Inferred Services
Service Maps support Inferred Services, which are services detected via traces but may not be directly instrumented.
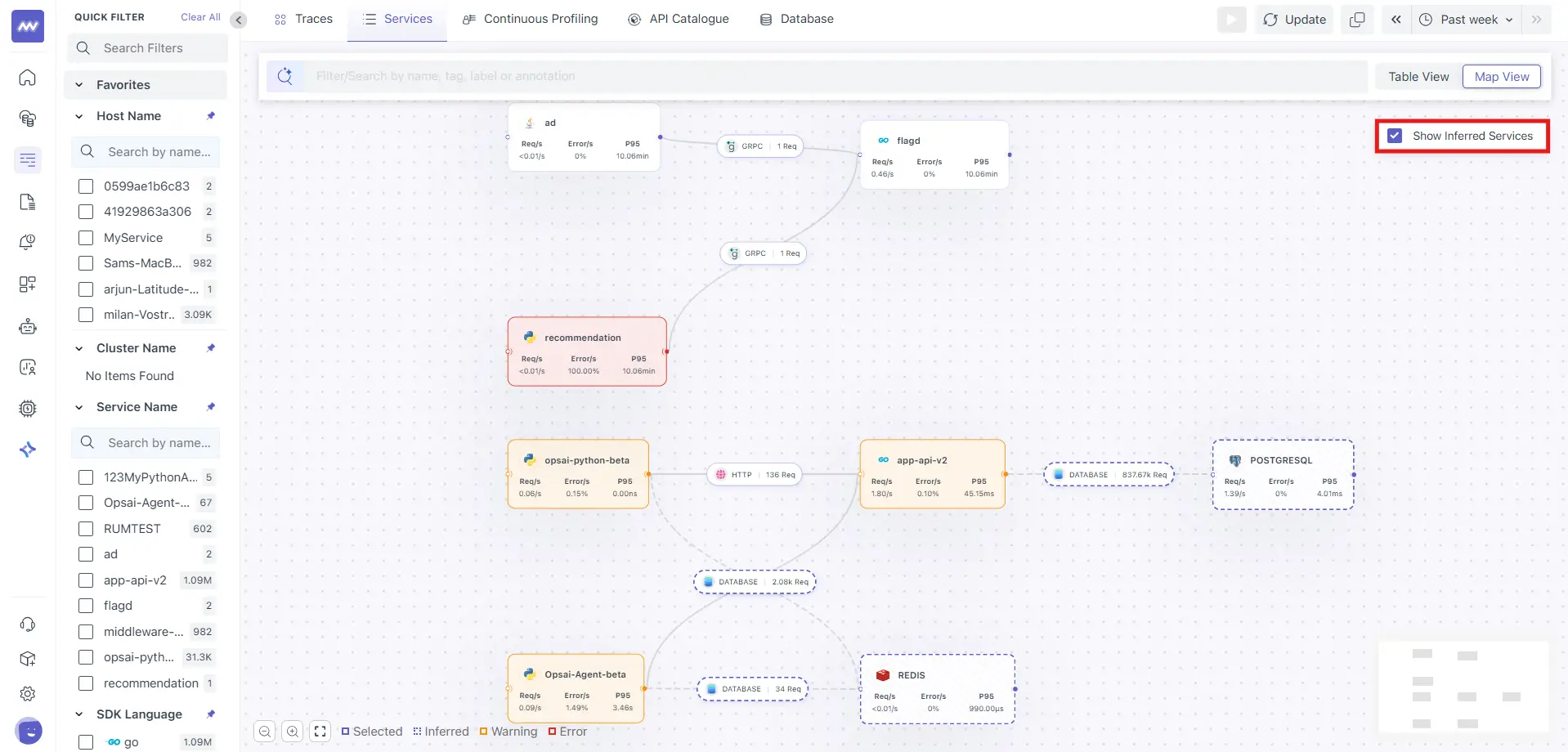
Show Inferred Services Toggle
- Enable Show Inferred Services to display:
- Databases (PostgreSQL, Redis, etc.)
- External APIs
- Third-party dependencies
Inferred services are shown with dashed borders, helping you distinguish them from fully instrumented services.
When to Use Service Maps
- Service Maps are especially useful when:
- Investigating latency spikes
- Debugging cross-service failures
- Understanding complex microservice architectures
- Onboarding new engineers to your system
- Performing impact analysis during incidents
Need assistance or want to learn more about Middleware? Contact our support team at [email protected].